Fig. 12.
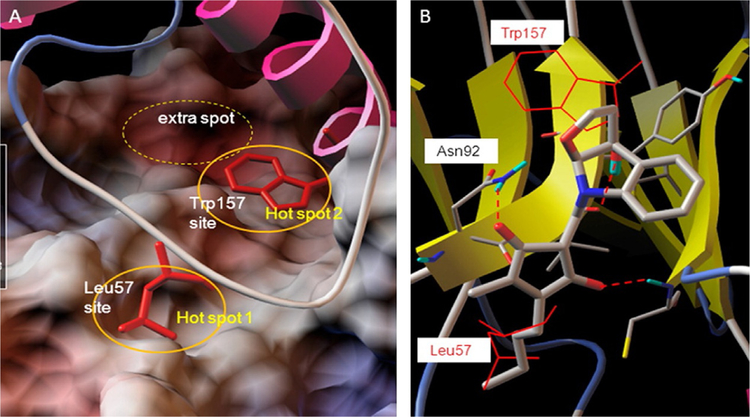
Hot spots at the interface of PPI in the IL-6/GP130 D1 domain. Modeling of binding hot spots at the IL-6/GP130 D1 domain interface. (A) D1 domain is represented as electrostatic potential surface (red, negatively charged; blue, positively charged; white, hydrophobic). IL-6 is in ribbon representation. The two larger yellow eclipses indicate the two main binding “hot spots,” Leu57-binding site and Trp157-binding site, between IL-6 and GP130. (B) Binding modeling of MDL-A to the GP130 D1 domain. D1 domain is in ribbon representation, and MDL-A is in thick ball-and-stick rendering. Hydrogen bonds are shown as red dotted lines. MDL-A disrupts both binding spots of the GP130 D1 domain. MDL-A forms three hydrogen bonds with Asn92, Cys6, and the carbonyl backbone of Val93 residues of GP130. The modeling indicates that the long butyl tail of MDL-A displaces Leu57 (thin red line), and the indoline moiety partially disrupts Trp157 (thin red line) of the helix D of IL-6. Reproduced with permission from Li, H., Xiao, H., Lin, L., Jou, D., Kumari, V., Lin, J., & Li, C. (2014). Drug design targeting protein-protein interactions (PPIs) using multiple ligand simultaneous docking (MLSD) and drug repositioning: Discovery of raloxifene and bazedoxifene as novel inhibitors of IL-6/GP130 interface. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 57(3), 632–641. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm401144z. Copyright (2014) American Chemical Society.