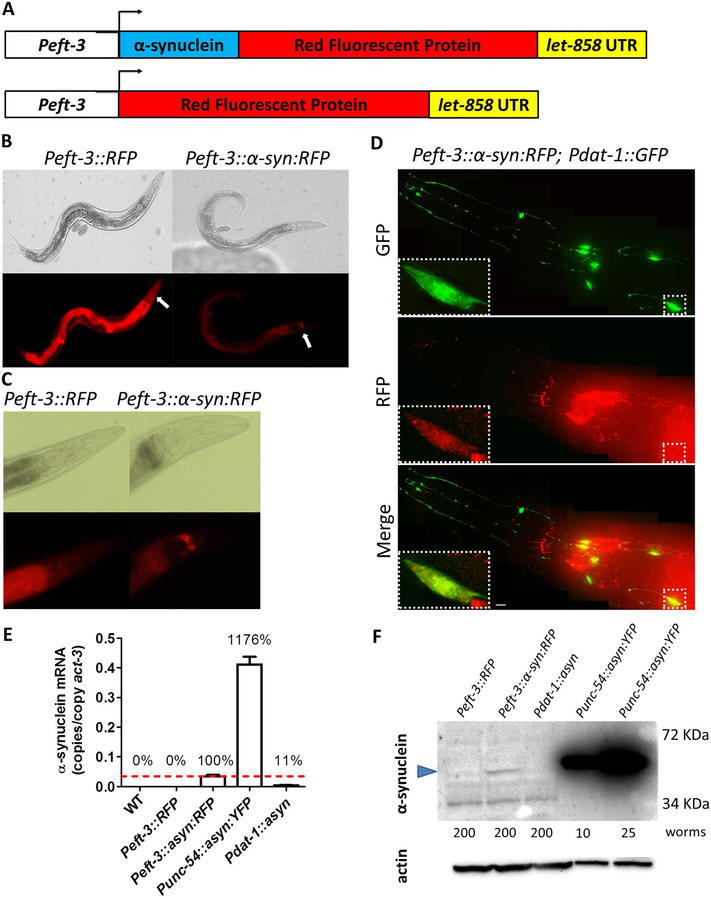
Fig. 1. Ubiquitously expressed α-synuclein::RFP fusion protein is present in dopamine neurons and accumulates in the nerve ring.
A. Diagram illustrating constructs used to generate C. elegans models that ubiquitously express α-synuclein linked to RFP and control strains expressing RFP alone. Both transgenes are expressed behind a ubiquitous promoter eft-3. B,C. Peft-3::RFP and Peft-3::α-syn:RFP worms exhibit expression of RFP and α-syn:RFP, respectively, in all tissues. Peft-3::α-syn:RFP show an accumulation of α-syn:RFP in the nerve ring that is not present in the RFP control strain. The nerve ring is indicated by the white arrows. D. α-syn:RFP exhibits colocalization with GFP expressed in dopamine neurons using dat-1 promoter indicating that α-synuclein is being expressed in dopamine neurons. Scale bar indicates 5 αm. E. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR demonstrates that α-synuclein mRNA is being expressed at a much lower level than Punc-54::α-syn:YFP worms, which express α-synuclein from an integrated multi-copy array. F. Western blotting using H3C anti-α-synuclein antibody shows that α-synuclein is being expressed in Peft-3::α-syn:RFP worms at a much lower level than Punc-54::α-syn:YFP worms. Blue arrow indicates α-synuclein band. A non-specific band of lower molecular weight was observed (also present in Peft-3::RFP control worms). The number of worms used for each lysate is indicated. Error bars indicate SEM.