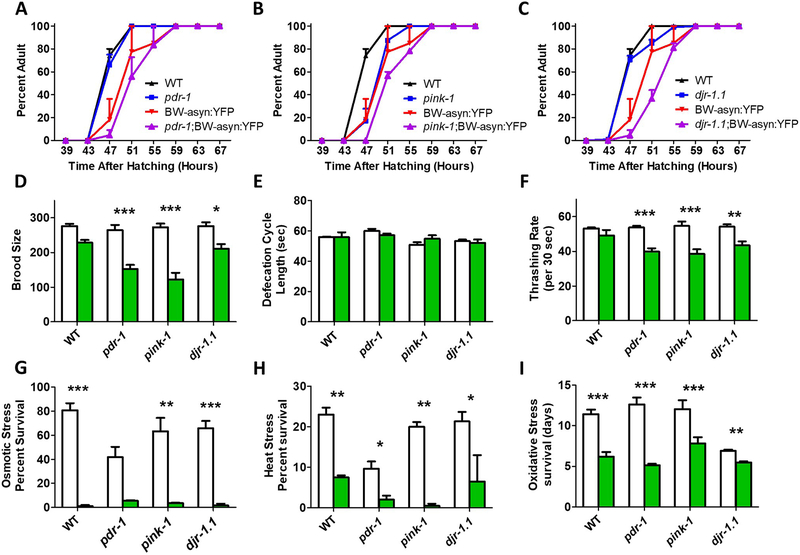
Fig. 8. Expression of α-synuclein in body wall muscle of recessive loss of function Parkinson’s disease mutants causes behavioral deficits and increased sensitivity to stress.
A-C. α-synuclein expression in body wall muscle caused a trend towards slowed development in pdr-1, pink-1 and djr-1.1 mutants. B. The expression of α-synuclein in body wall muscle decreased fertility in pdr-1 and pink-1 mutants to a greater extent than in WT (D), but had no effect on defecation rate (E) Green bars indicate BW-asyn:YFP background while white bars indicate wild-type background. F. Expressing α-synuclein in body wall muscle significantly decreased the rate of thrashing in pdr-1, pink-1 and djr-1.1 mutants but not in WT worms. Finally, α-synuclein expression in body wall muscle caused increased sensitivity to osmotic stress (G, 500 mM NaCl), heat stress (H, 37°C) and oxidative stress (I, 4 mM paraquat) independent of strain background. Punc-54::α-syn:YFP worms are indicated as BW-asyn:YFP . Error bars indicate SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.