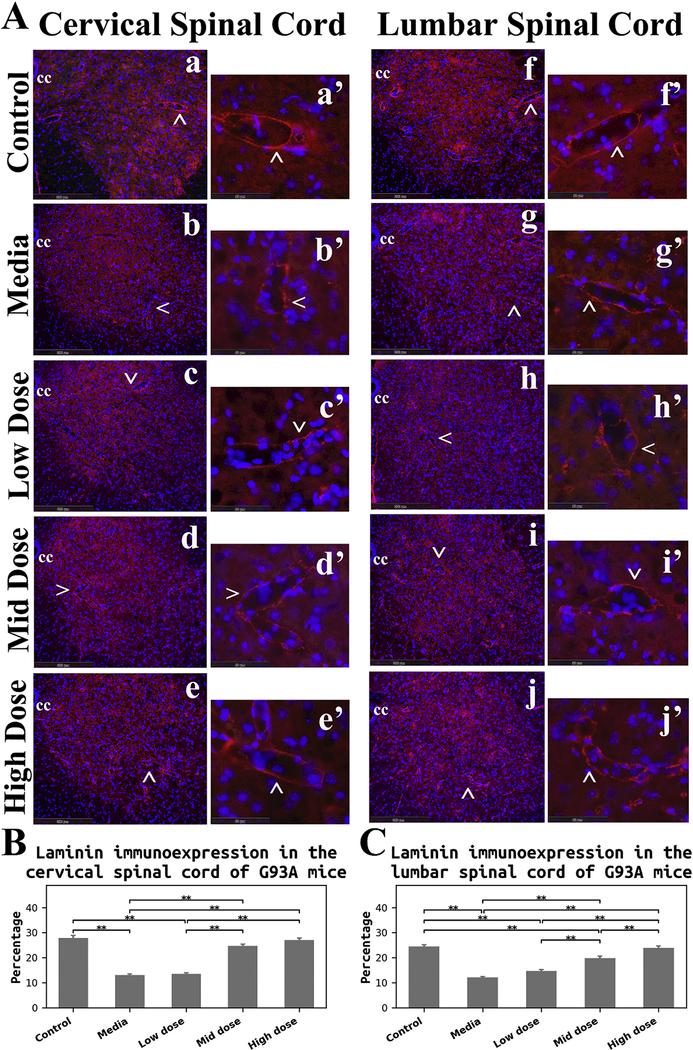
Figure 6. Immunohistochemical analysis of laminin in the spinal cord of G93A mice.
(A) Immunofluorescence staining for laminin in the spinal cords. In control mice, immunostaining for laminin (red) demonstrated well organized microvasculature networks in the cervical (a) and lumbar (f) ventral horns. Spinal cord capillaries displayed a continuous layer of laminin immunoexpression (red, cervical: a’, lumbar: f’) in these animals. Substantial reductions of laminin immunoexpression (red) in microvessels were determined in both cervical (b) and lumbar (g) spinal cords of media-treated ALS mice. Irregularities of laminin staining were obvious in the ventral horn of cervical (b’) and lumbar (g’) spinal cords. ALS mice receiving the low cell dose showed similar patterning of laminin immunoexpression (red) in the spinal cords (cervical: c, c’, lumbar: h, h’) as in media mice. Increased numbers of capillaries with adequate laminin expression (red) were observed in the cervical and lumbar spinal cords of mice-treated with mid (cervical: d, d’, lumbar: i, i’) and high (cervical: e, e’, lumbar: j, j’) cell doses. More robust capillary laminin staining was apparent after the high cell-dose treatment (red, cervical: e’, lumbar: j’) vs. mid cell-dose. The locations of high magnification images of capillaries in a’, b’, c’, d’, e’, f’, g’, h’, i’, and j’ are indicated by arrows in a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h, i, and j. cc – central canal. The nuclei in all images are shown with DAPI. Scale bar in a-j is 200 μm, in a’-j’ is 50 μm. (B) Quantitative analysis of laminin immunoexpressions in the cervical ventral horn. Media-treated mice showed a significant reduction of laminin expression vs. controls. There were no significant differences between the low cell-dose treatment and media mice. Yet, mice receiving the mid and high cell-doses demonstrated significant increases of laminin immunostaining vs. media-treated or low cell-treated animals. (C) Quantitative analysis of laminin immunoexpressions in the lumbar ventral horn. A significant decrease of laminin detection was determined in media mice, similar to findings in the cervical spinal cord. Although no significant differences were found in mice receiving the low cell-dose compared to media, significantly elevated laminin immunostaining was detected in mice treated with the mid and high cell-doses vs. media and low cell-dose. Also, high cell-dose mice showed significantly higher percentage of laminin expression compared to mid cell-dose treated animals. **p < 0.01.