Fig. 5. IL-2c treatment attenuates biliary injury and liver fibrosis.
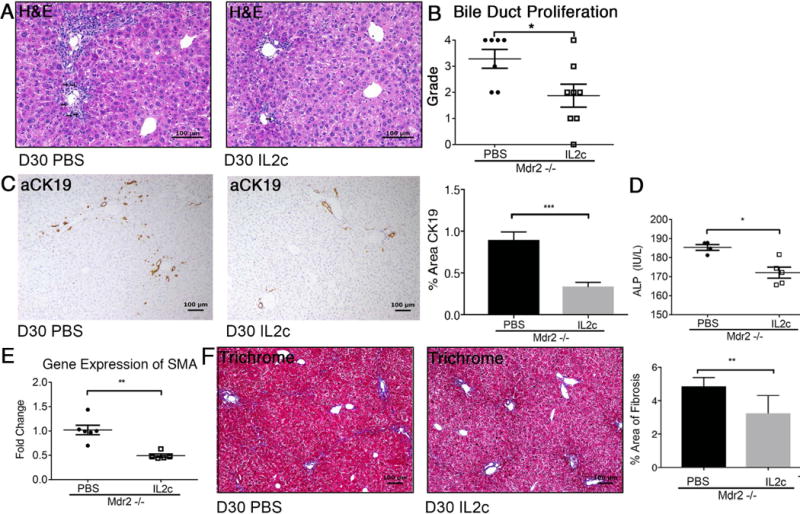
Liver histopathology was assessed in 30-day-old male Mdr2−/− mice following treatment with IL-2c vs PBS between day 7 and 30. Arrows denote bile duct profiles on representative photomicrographs of H&E stained liver sections (A). Bile duct proliferation was graded by pathologists using a semi-quantitative scale from 1-4 (B). Liver sections were subjected to anti-CK-19 immunohistochemistry and subsequent image analysis (C). Serum ALP was measured in 30-day-old Mdr2−/− mice using a colorimetric assay (D). Real-time PCR was performed for the pro-fibrogenic gene SMA from cDNA synthesized from whole liver RNA (E). Trichrome-stained liver sections of Mdr2−/− mice treated with IL-2c verses PBS were analyzed utilizing Aperio Image Analysis to determine percent area of liver fibrosis (F). Statistical significance was assessed with an unpaired t test with *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.005.
