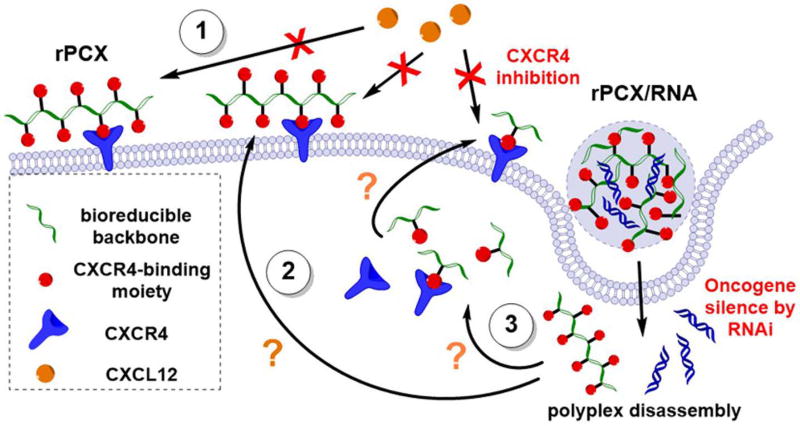
Figure 6.
Proposed mechanisms of PCX/RNA polyplexes. (1) Excess PCX of the polyplexes formulation is responsible for the immediate CXCR4 antagonism. (2) The disassembly of polyplex releases both small RNA and PCX. Functional small RNA silences oncogene through RNAi mechanism. These released PCX results in delayed CXCR4 inhibition effect via binding intracellular CXCR4 during recycling or via PCX excretion from the cells and binding the plasma membrane CXCR4 on cancer cells. (3) In case of intracellularly bioreducible PCX (rPCX), the small molecule degradation products containing the CXCR4-binding cyclam moieties further contribute to the CXCR4 inhibition.