Figure 1.
Genome-wide Association Study Identifies the Main Color Pattern Locus in H. axyridis
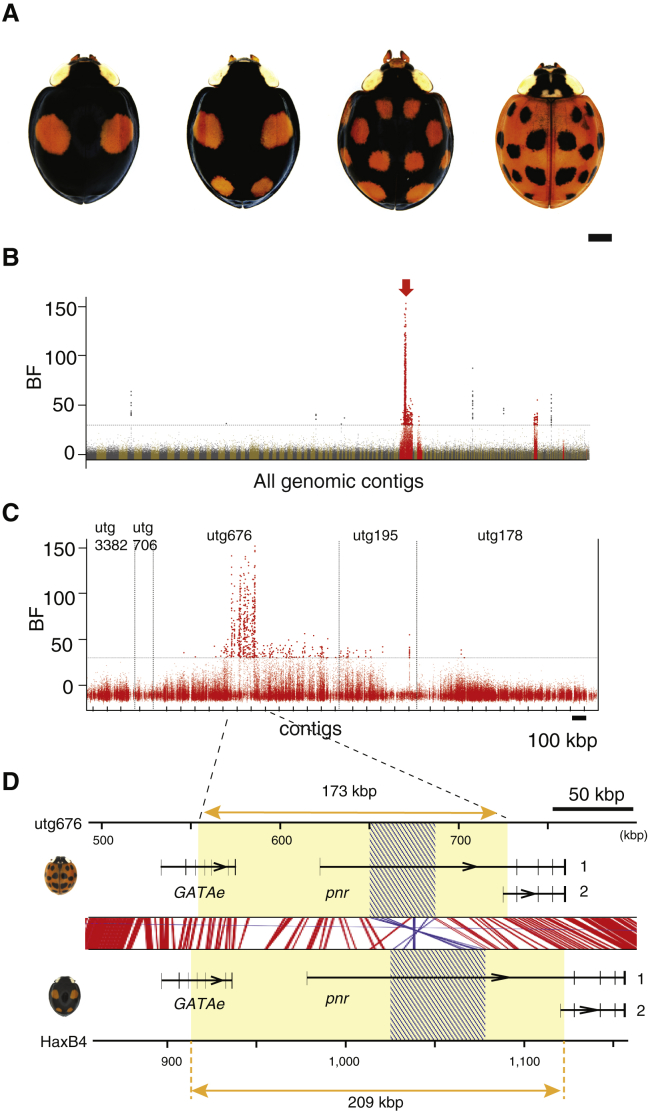
(A) The four most frequent color pattern forms of H. axyridis. From left to right: the form Black-2Spots (f. conspicua), Black-4Spots (f. spectabilis), Black-nSpots (f. axyridis), and Red-nSpots (f. succinea).
(B) Manhattan plots of genome-wide association for the proportion of Red-nSpots individuals in 14 DNA pooled samples of wild H. axyridis populations, with Bayes factor (BF) for individual SNPs. The horizontal dashed line indicates the 30 deciban (db) threshold. SNPs above this threshold are highlighted, and those assigned to contig utg676 (red arrow, containing the color pattern locus) in the HaxR assembly and four neighboring contigs are shown in red. Contigs are ordered by length, and only autosomal contigs are shown.
(C) Same as (B), with a focus on SNPs belonging to the five neighboring contigs including and surrounding the color pattern locus of the HaxR assembly (in red in Figure 1B). The relative ordering of these contigs was derived from the de novo sequencing of the Black-4Spots allele extended region (see STAR Methods).
(D) The gene content at the identified color pattern locus. Fifty-six SNPs with the strongest association signal delimit a candidate color pattern locus region of ∼170 kb (yellow boxes) that extends from the first coding exon of pannier (pnr) to the 5′ upstream gene GATAe. Red and blue lines show conserved sequence blocks in forward or reverse direction, respectively, detected by [13]. The first intron of pannier contains the footprint of an ∼50 kb inversion (shaded boxes). Two alternative splice variants of pnr are produced (named 1 and 2).
See also Figures S1, S3, and S4.