Figure 2.
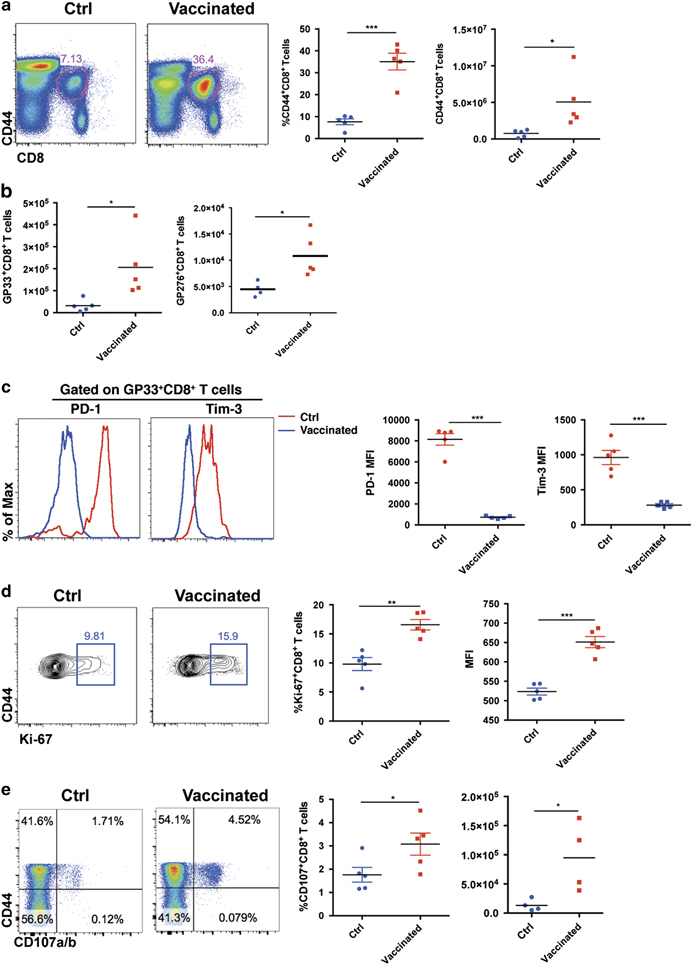
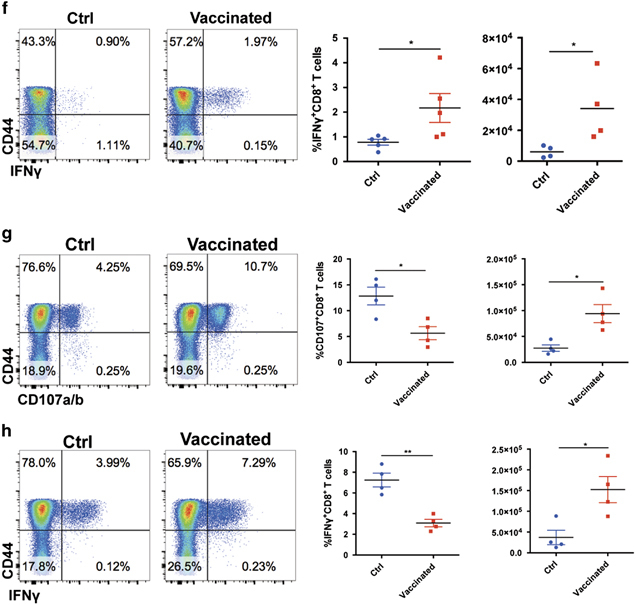
CD4+ T cell epitope-based heterologous prime-boost vaccination recruited exhausted CD8+ T cells during chronic viral infection. On day 8 post boost: (a) The frequencies and numbers of virus-activated CD44hiCD8+ T cells in the spleens of the control and vaccinated mice (n=5). (b) The numbers of LCMV-GP33- and LCMV-GP276-specific CD8+ T cells in the spleens of the control and vaccinated mice (n=5). (c) PD-1 and Tim-3 expression in the virus-specific CD8+ T cells of the control and vaccinated mice (n=5). MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. (d) The expression of Ki-67 in the CD44hiCD8+ T cells of the control and vaccinated mice (n=5). (e–h) Upon stimulation with LCMV-specific peptides, the frequency and number of surface CD107a/b+- and IFN-γ-producing CD8+ T cells in the spleens of the control and vaccinated mice (e, f: stimulated by GP33–41, n=5; g, h; stimulated by GP276–286, n=4). The data are representative of three independent experiments and were analyzed using two-tailed unpaired t-tests (b–f). The error bars (b–f) denote the s.e.m. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.
