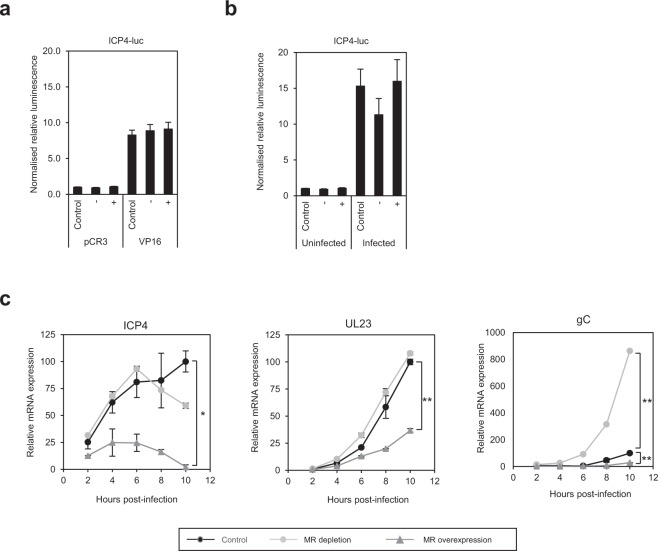
Figure 4.
The MR affects transcription of viral genes at early stages post-infection. (a) The MR does not affect basal transcription of the ICP4 promoter. The MR was depleted (−) or overexpressed (+) in HeLa cells, before transfecting with control pCR3 or a pCR3-VP16 expression plasmid and an ICP4-luciferase plasmid. After 24 hr, luciferase activity was measured and normalised to controls (pCR3 plasmid alone). Error bars represent the standard error of at least three experiments carried out in triplicates. (b) The MR does not affect transcription of the ICP4 promoter during infection. The MR was depleted (−) or overexpressed (+) in HeLa cells before transfecting with an ICP4-luciferase plasmid. After 24 hr cells were infected with HSV-1 (MOI 1), luciferase activity measured after 8 hr and normalised to uninfected controls (RSCF siRNA or pCR3 plasmid). Error bars represent the standard error of at least three experiments carried out in triplicates. p-values for statistical significance were calculated by unpaired two-tailed t-test for unequal variances. *p ≤ 0.001. (c) The MR does not directly affect IE gene expression. The MR was depleted or overexpressed in HeLa cells before infecting with HSV-1 (MOI 1). RNA was extracted at 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 hr post-infection and expression of HSV-1 genes from each temporal class (immediate-early, ICP4; early, UL23; late, gC) was quantified by RT-qPCR, normalised to the house-keeping gene HPRT and calibrated to control (RSCF siRNA or pCR3 transfected) cells at 2 hr post-infection. Error bars represent the standard error of duplicates and is representative of three independent experiments. p-values for statistical significance were calculated by unpaired two-tailed t-test for unequal variances. *p < 0.04; ** ≤ 0.001.