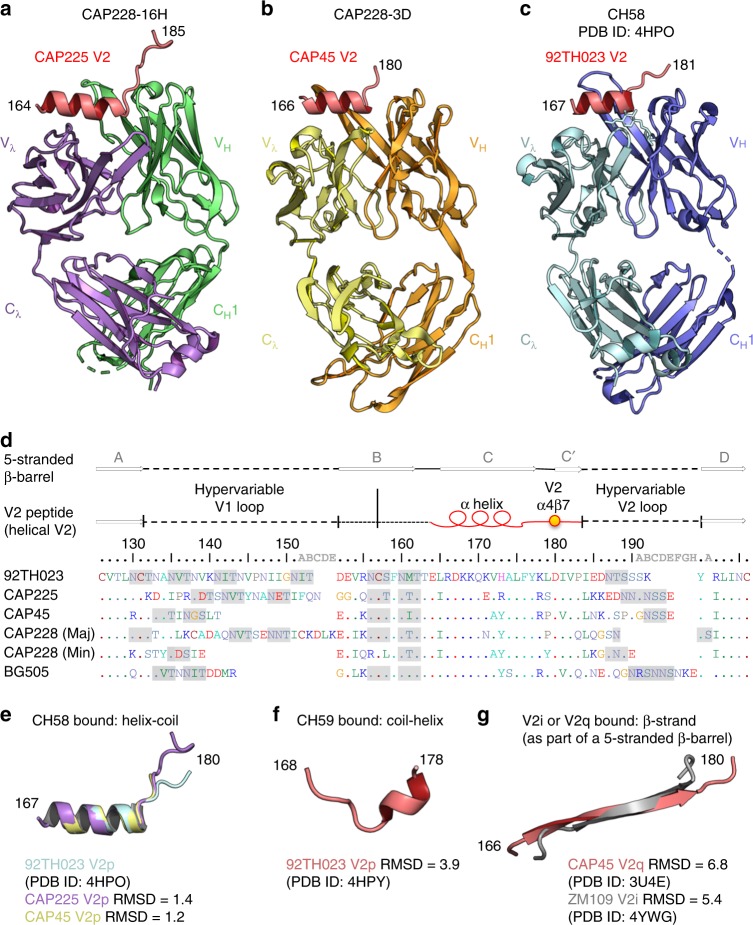
Fig. 1.
HIV-1 V2 peptides reproducibly sample the same helix-coil conformation. a A cartoon representation of the Fab region from V2p mAb CAP228-16H bound to a heterologous V1V2 domain from HIV-1 strain CAP225. Only V2 residues 164–185 were resolved, and are shown in red. The Fab heavy and light chains are coloured green and purple, respectively. b A cartoon representation of the Fab region from V2p mAb CAP228-3D bound to a short, heterologous V2 peptide (shown in red) from HIV-1 strain CAP45. The Fab heavy and light chains are coloured orange and yellow, respectively. c Previously determined cocrystal structure of CH58 bound to the RV144 vaccine strain V2 peptide. d A sequence alignment of the V1V2 domains from the HIV-1 strains for which crystal structures were determined in this study, as well as the dominant (Maj) and subdominant (Min) CAP228 cofounder viruses. The hypervariable loop regions of V1 and V2 are indicated with the dashed lines, while the conserved V2 helix-coil motif is labelled with a red cartoon representation. A gold sphere was used to mark the location of the primary α4β7 binding site, and any potential N-linked glycosylation sites are shaded grey. Above, arrows designate those regions of V1V2 that form the 5-stranded β-barrel bound by V2q/V2i mAbs. e Main chain superimposition of the V2 peptides (residues 167–180) bound by CAP228-16H (purple), CAP228-3D (yellow) and CH58 (light blue). The Cα root-mean-square deviation for each comparison with CH58 bound peptide is shown. f Previously determined structure of a CH59 bound V2 peptide (residues 168–178). g Previously determined structures of the V2 C-sheet in the context of the 5-stranded β-barrel (residues 166–180) when bound by PG9 (red) or 830 A (silver)