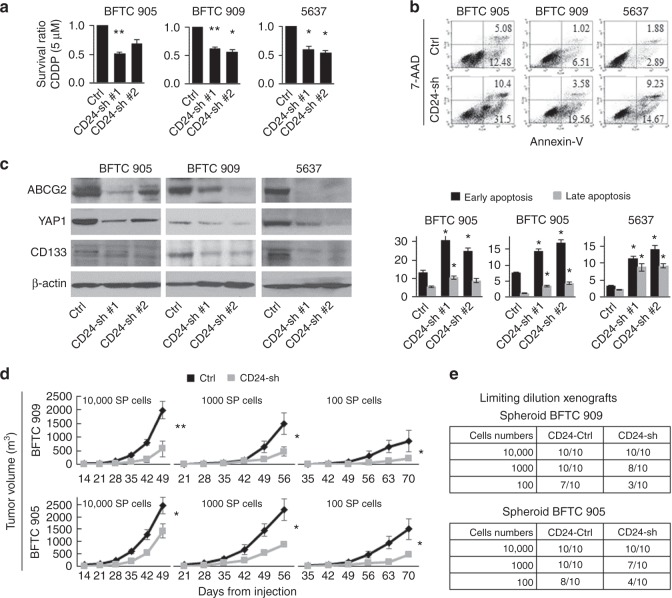
Fig. 2.
The chemoresistant and tumorigenic abilities attenuated by CD24 knockdown in BFTC 905, BFTC 909, and 5637 cell lines. a Cell viability after 5 μM cisplatin (CDDP) treatment for 72 h in the spheroid CD24-sh cells, as measured by MTT assay. Cell viability was expressed as the ratio of absorbance values of the spheroid CD24-sh cells related to the spheroid CD24-Ctrl cells considered as 1.0. Data are from three independent experiments. b An apoptosis assay of spheroid CD24-sh cells treated with 5 μM CDDP for 72 h. Upper, representative images of early apoptosis (bottom right quadrant) and late apoptosis (top right quadrant); lower, percentage of apoptotic cells. c Western blotting analysis of ABCG2, YAP1, and CD133 in stable CD24-sh and CD24-Ctrl cells. d Limiting-dilution xenograft assays in stable spheroid CD24-sh BFTC 909 (upper) and BFTC 905 (lower) cells. Tumour growth was measured after subcutaneous injection of serially diluted spheroid cells (1 × 104, 1 × 103, or 1 × 102 cells per flank) into both flanks of NSG mice (five mice per group). SP, spheroid. e Tumour initiation frequency after the xenotransplantation of spheroid CD24-sh BFTC 909 (upper) and BFTC 905 (lower) cells. Tumour-initiating capacity is shown as the numbers of tumours/the number of injections after 70 days from subcutaneous injection of serially diluted spheroid CD24-sh cells (1 × 104, 1 × 103, or 1 × 102 cells per flank) into both flanks of NSG mice (five mice per group). Each error bar indicates mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 (Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test)