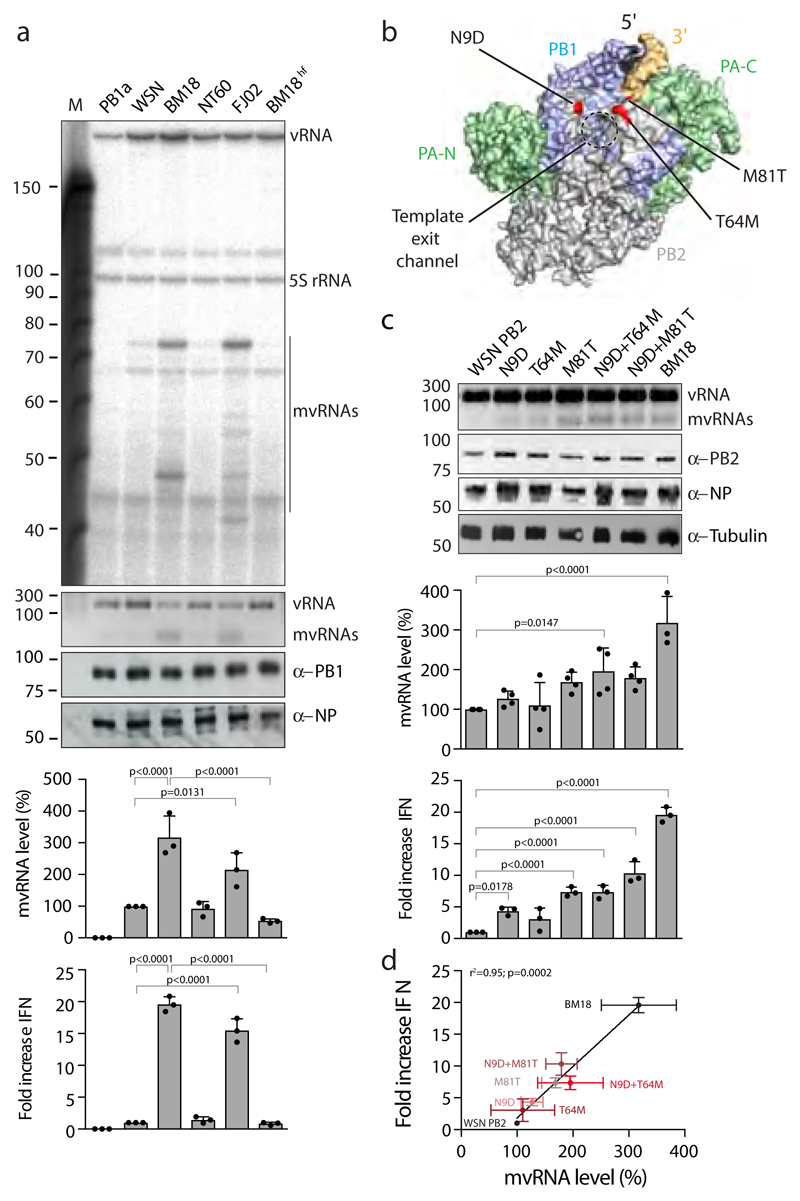
Figure 3. The PB2 polymerase subunit of highly virulent influenza A viruses promotes mvRNA synthesis.
(a) Analysis of mvRNA levels using primer extension (top gel) or RT-PCR (second gel) during the replication of a segment 5-based 246 nt RNA template by the WSN, BM18, NT60 and FJ02 polymerases, and IFN-β promoter activity induced by the transfection of total RNA isolated from these cells into reporter HEK 293T cells expressing luciferase. NP and PB1 expression was assessed by western blot. n=3 biologically independent experiments. P-values were determined using ANOVA with adjustments for multiple corrections compared to WSN. (b) Location of PB2 amino acid residues 9, 64 and 81 in the bat influenza A virus polymerase structure (PDB 4WSB). (c) Analysis of the effect of PB2 mutations on mvRNA formation using RT-PCR (top gel) and IFN-β promoter activity induced after transfection of total RNA isolated from these cells into luciferase reporter HEK 293T cells. PB2, NP and tubulin expression was analysed by western blot. P-values were determined using ANOVA with adjustments for multiple corrections compared to WSN. n=4 biologically independent experiments for all WSN mutants in top graph. n=3 biologically independent experiments for BM18 in top graph and all samples in bottom graph. (d) IFN-β promoter activity as function of PB2 mutation and mvRNA formation. Each data point was generated using the biologically independent experiments presented in c. P-values were determined using linear regression. All graphs show standard deviation and mean.