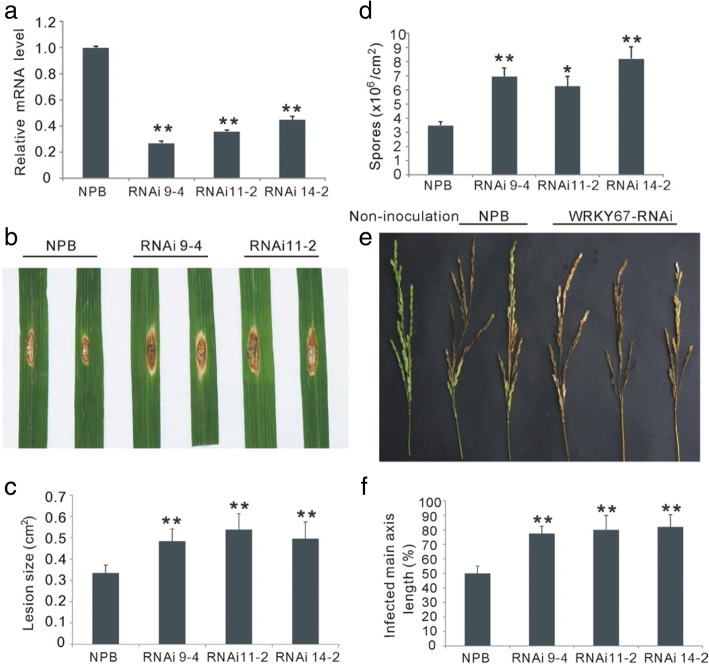
Fig. 4.
Phenotypes of the OsWRKY67-silenced (WRKY67-RNAi) plants infected with blast fungus. The asterisks represent significant differences relative to wild-type Nipponbare (NPB) plants (t-test, **P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05). a Relative transcription levels of OsWRKY67 in Nipponbare and WRKY67-RNAi plants. The values are means ± SDs of three biological replicates. b Silencing of OsWRKY67 increased susceptibility to leaf blast infection using punch method. c Relative lesion size in Nipponbare and WRKY67-RNAi plants after leaf blast infection. The values are means ± SDs of twelve biological replicates. d Numbers of spores produced on Nipponbare and WRKY67-RNAi plants after punch inoculation. The values are means ± SDs of six biological replicates. e Silencing of OsWRKY67 increased susceptibility to panicle blast in rice. f The infected main axis length in Nipponbare and WRKY67-RNAi plants after panicle blast inoculation. The values are means ± SDs of twelve biological replicates