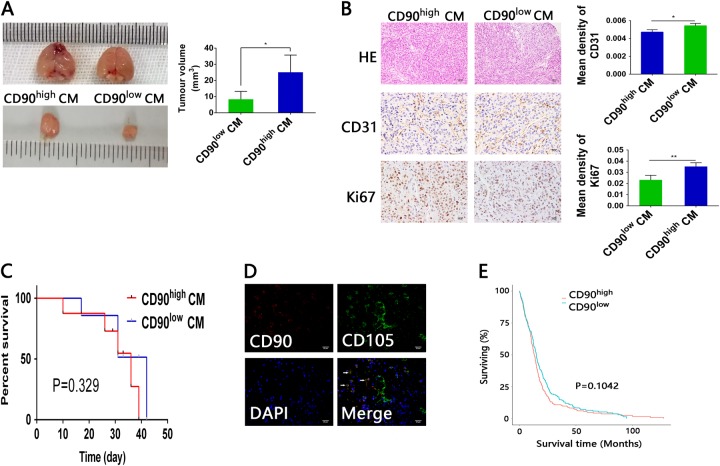
Fig. 5. Conditioned media from CD90high and CD90low gbMSCs have different functions in vivo.
a Representative mice from intracranial xenograft experiments in which U87 cells with CD90high CM (left) or U87 cells with CD90low CM (right) were injected into the right frontal lobes of nude mice. Obviously, the sizes of the CD90high CM group tumours were greater than those of their CD90low CM counterparts. *P < 0.05. b Both the CD90high CM and CD90low CM tumour sections were stained with HE (×200, scale bars = 50 μm). In the CD90high CM and CD90low CM tumour tissues, IHC was employed to detect CD31 and Ki-67 expression (×400, scale bars = 25 µm). (n ≥ 3) *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. c Survival curves of glioma-bearing mice. The survival times of mice implanted with U87 cells cultured with CD90high CM were not significantly shorter than those of mice implanted with U87 cells cultured in CD90low CM. d Double staining for CD105 (green) and CD90 (red) revealed that CD105+CD90− cells were located in the vessel walls, whereas CD105+CD90+ cells were located around the tumour parenchyma. (×400, scale bars = 25 µm). e Kaplan–Meier survival curves for patients with low and high CD90 expression. The survival of glioma patients with different CD90 expression levels in TCGA database was not significantly different