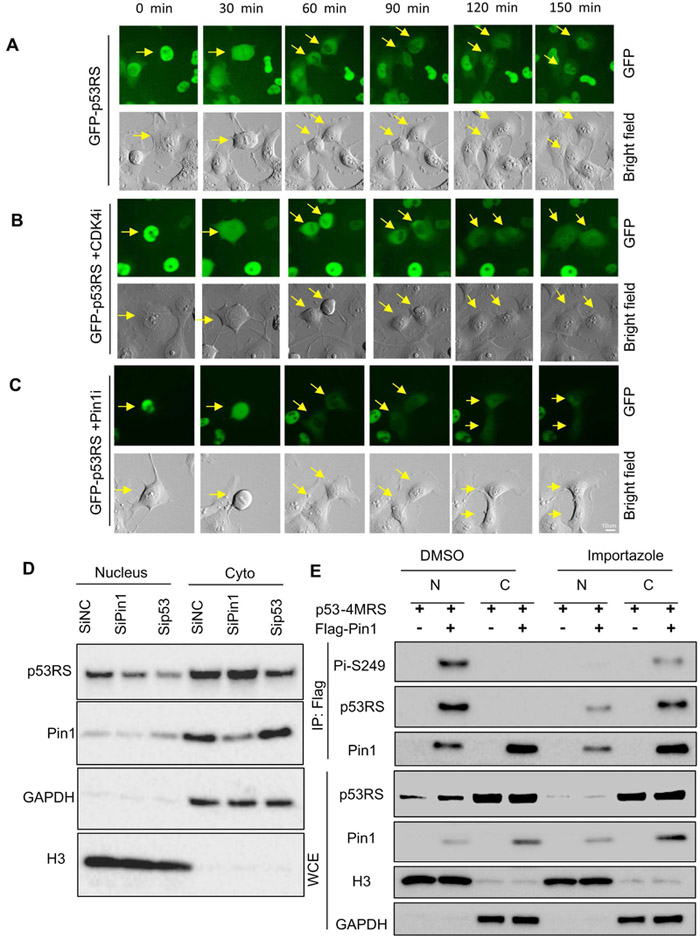
Figure 3. Nuclear localization of phosphorylated p53-RS is dependent on Pin1.
A) Time-lapse analysis of GFP-p53 in H1299. GFP-p53-RS was stably expressed in H1299 cells. Frames show the GFP-p53-RS subcellular localization; Arrows indicate the one cell division in mitosis to two daughter cells in G1 phase. For each sequence, t=0 min is the first frame marked by the arrow were observed. Scale bar, 10um. The same for panels B and C below.
B) Time-lapse analysis of GFP-p53 after treatment of 500 nM CDK4 inhibitor (CDK4i) in H1299 cells.
C) Time-lapse analysis of GFP-p53 after treatment with 5 μM Pin1 inhibitor (Pin1i) in H1299 cells.
D) Knockdown of Pin1 decreases nuclear p53-RS level. PLC/PRF/5 cells were transfected with siRNA for Pin1 (SiPin1) or p53-RS (Sip53), and used for subcellular fractionation 72 h after transfection, followed by WB with indicated antibodies.
E) Nuclear translocation of phosphorylated p53-RS is blocked by a transport inhibitor Importazole. H1299 cells were transfected with combination of plasmids encoding p53-4MRS, and/or Flag-PIN1 and treated with Importazole overnight before harvesting for analysis of subcellular fractions by co-IP with IgG or a p53 antibody followed by WB with indicated antibodies.