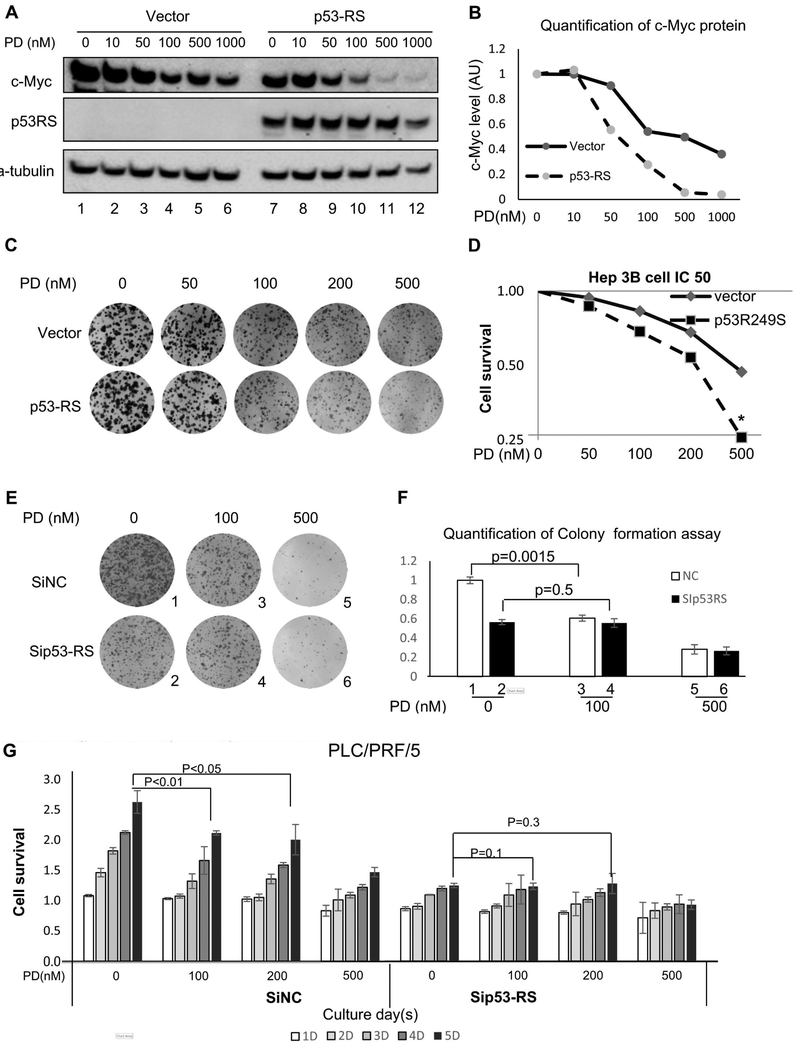
Figure 6. CDK4 inhibitor alleviates p53-RS-dependent cell proliferation.
A) and B) p53-RS can sensitize the reduction of c-Myc protein level by a CDK4 inhibitor, PD033291 (PD). The control or p53-RS plasmid was introduced into p53-null Hep3B HCC cells. Cells were treated by PD for 24 h and harvested for WB with indicated antibodies (A), and the quantification of c-Myc protein level is shown in the graph (B). c-Myc level was quantified against the level of a-tubulin. AU=arbitrary unit.
C) and D) p53-RS makes Hep3B HCC cells more sensitive to the CDK4 inhibitor PD. The control or p53-RS plasmid was introduced into Hep3B cells. Cells were treated by different concentrations of PD for Colony formation assay (C), or cell survival analysis by a WST cell growth kit (D). IC50 values are represented as mean ± SD (n = 3) (D).
E) and F) Knockdown of p53-RS makes PLC/PRF/5 HCC cells less sensitive to the CDK4 inhibitor PD. SiNC or Sip53 was introduced into PLC/PRF/5 cells, and then treated by different concentrations of PD for colony formation assay (E). The quantification of colonies is shown in the graph (F). P values were calculated for the data between columns 1 and 3 (p = 0.0015) and between columns 2 and 4 (p = 0.5), respectively.
G) Cell survival analysis was also conducted in the same set of experiments with different doses of PD by using a WST cell growth kit. Cell survival rates are represented as means ± SD (n = 3) for each time point (D = day, such as 5D = 5 days). P values were calculated as shown on top of the columns.