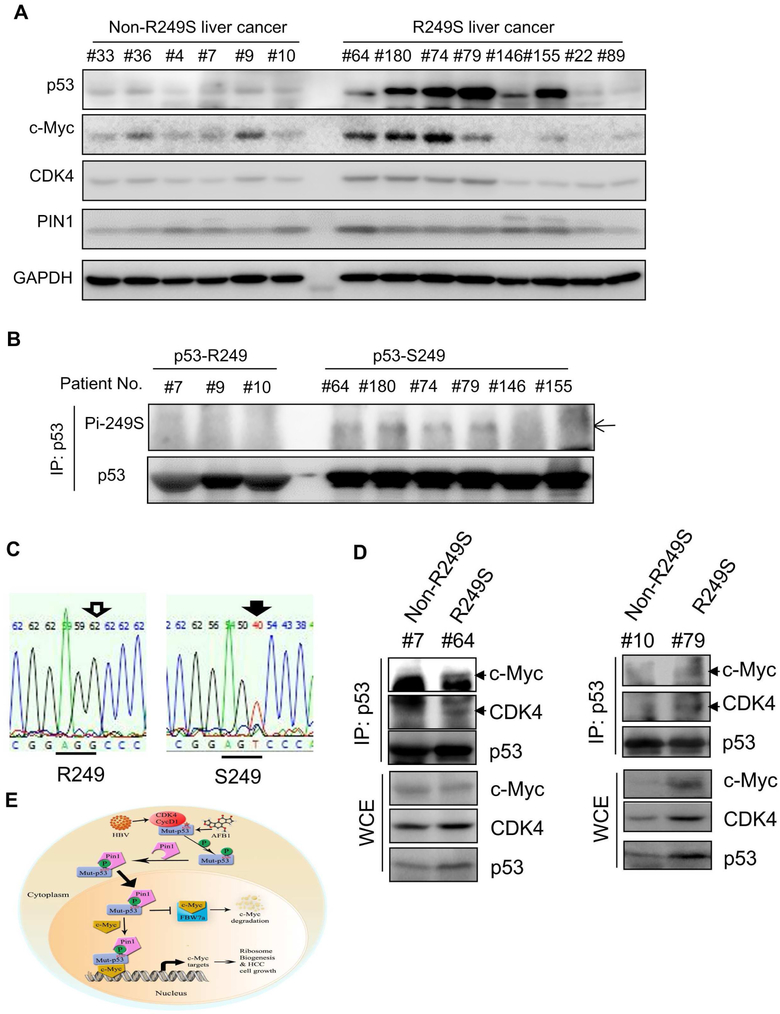
Figure 7. Phosphorylation of p53-R249S is well correlated with high levels of CDK4, Pin1 and c-Myc in primary human HCCs.
A) Concurrence of high expression of p53-R249S, c-Myc and CDK4 in HCCs. Equal amounts of HCC samples with or without p53-R249S were analyzed by WB with indicated antibodies.
B) p53-R249S is phosphorylated in HCCs. HCC samples from Panel A were subjected to IP using the anti-p53 DO-1 followed by WB with the anti-phosphor-S249 antibody and the rabbit monoclonal anti-p53 EPR17343 for total p53 protein level, respectively (of note, equal amounts of total p53 protein inputs were used for IP-WB for all HCC tissues used here by increasing 5-6 fold more total proteins in wt p53 containing HCCs than in p53-RS-containing HCCs).
C) R249S mutations were identified in HCC specimens by TP53-Exon 7 sequencing.
D) p53-R249S binds to c-Myc and CDK4 in primary HCCs. HCC samples with or without p53-R249S mutation were subjected to co-IP-WB assays with the anti-p53 antibody, and bound proteins were detected by WB with indicated antibodies. The input proteins were presented in the lower panels, and arrowheads point to target proteins.
E) A model for the CDK4-p53-R249S-PIN1-c-Myc signaling pathway in HCC.