Figure 1.
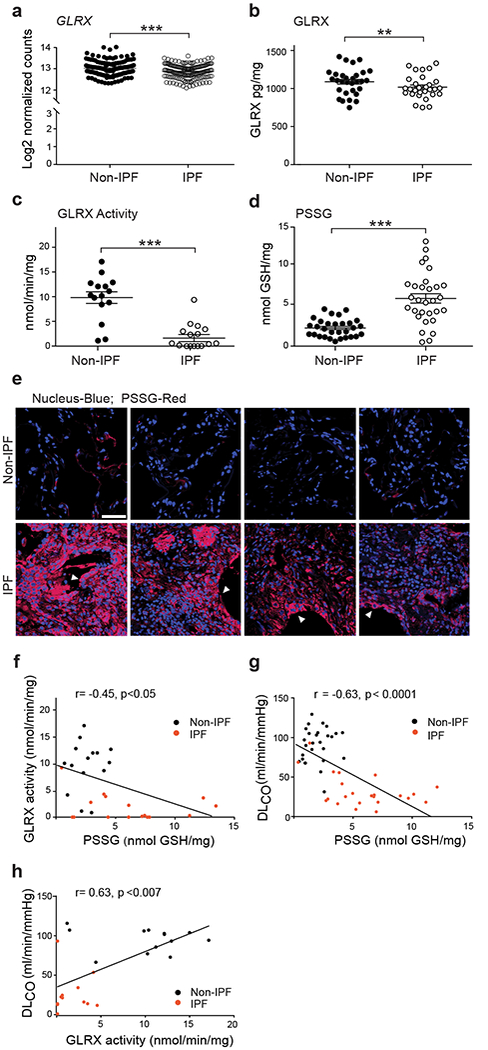
Lower glutaredoxin-1 (GLRX) enzymatic activity and higher protein S-Glutathionylation (PSSG) occur in lung tissues from subjects with IPF and correlate with disease severity. (a) mRNA expression of GLRX in lung tissue from subjects with IPF (n = 160) and without IPF (non-IPF; n = 132). *P < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis test. Supplementary Table 1 shows subject demographics. (b) GLRX protein in lung tissues from individuals without IPF (Non-IPF; n = 30) and with IPF (n = 29). (c) GLRX enzyme activity following its immunoprecipitation from lung tissues from subjects with IPF (n = 16) and without IPF (non-IPF; n = 15). Results are expressed as nmol/min/mg of input protein. (d) PSSG in lung tissue from cases of IPF (n = 30) and non-IPF (n = 30). (e) In situ PSSG (red) in healthy lungs (n = 4) or lung tissue from subjects with IPF (n = 4). Scale bar, 50μm. White arrowheads, reactive type II pneumocytes. (f-h)Correlations between PSSG and GLRX (f), PSSG and DLCO (g), and GLRX activity and DLCO (h), in lungs of subjects with IPF and non-IPF controls. Supplementary Table 2 shows demographics of subject samples used in panels b-h. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, 2-tailed Student’s t-test.
