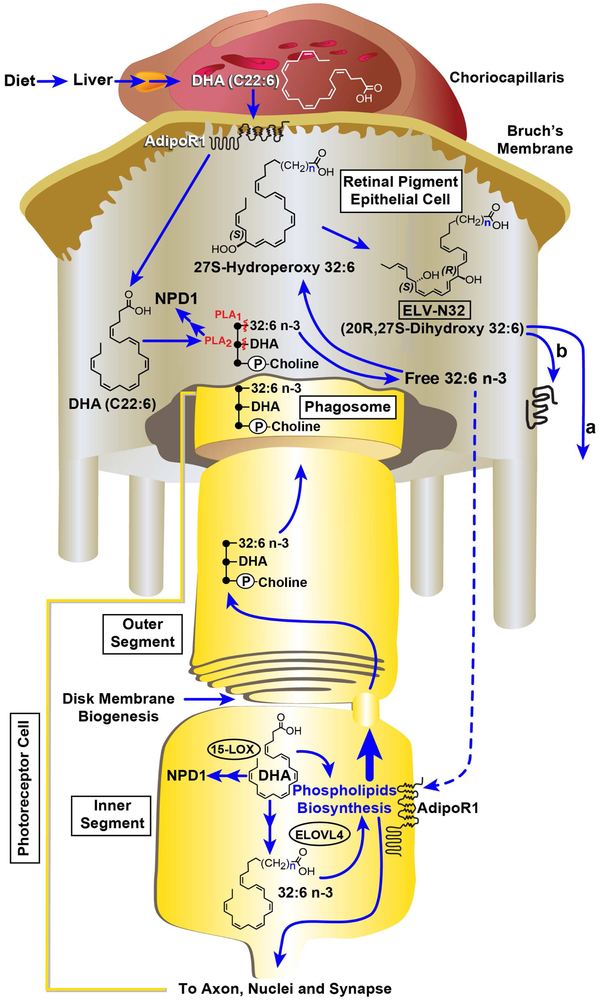
Fig. 1. Cell-specific ELV-synthesis and its targets.
The liver supplies DHA or 18:3 (not shown) from the diet. AdipoR1 captures DHA in the RPE as well as in the inner segments of PRCs. ELOVL4 generates 32:6 n-3 or 34:6 n-3 from EPA/DHA and other VLC-PUFAs,n-3. In this cartoon, for simplicity, only 32:6 n-3 synthesis to ELV-32 is highlighted, although 34:6 n3 follows a similar route toward the ELV 34 synthesis. In the inner segment the VLC-PUFAs,n-3 became acylated into C1 (sn-1) of phosphatidylcholine (PC, it also contains at sn-2 DHA). This phospholipid molecular species (PCMS) is used in the biogenesis of outer segment disc membranes, where the phospholipid tightly interacts with rhodopsin (Aveldaño, 1988). After shedding and phagocytosis by the RPE cells, the PC, upon impending disruptors of homeostasis, releases free 32:6 n-3 or 34:6 n-3 (by a Pl A1) and/or DHA (by a Pl A2). The 32:6 n-3 or 34:6 n-3 are then converted into ELVs following VLC-PUFAs,n-3 hydroperoxide intermediates. In 32:6 n-3 and ELV-N32, (CH2) n represents 11 carbons. Autocrine (A) / paracrine (B) pro-homeostatic signaling by ELVs sustain integrity of RPE and of PRC.