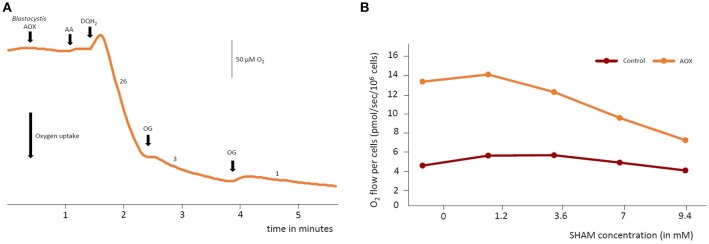
Figure 5.
Oxygen uptake by Blastocystis alternative oxidase (AOX) in Escherichia coli. (A) Oxygen levels were allowed to stabilize before addition of heme deficient E. coli membranes expressing recombinant Blastocystis AOX. Addition of duroquinol (DQH2) (final concentration of 1 mM) induced oxygen consumption. Oxygen uptake was sensitive to a typical AOX inhibitor octylgallate (OG). Octylgallate was added to a final concentration of 25 μM. Oxygen consumption was not due to the action of complex IV as protein was expressed in heme deficient E. coli and functional complex IV cannot be produced by these cells. Furthermore, antimycin A, a complex III inhibitor, was added (AA) to a final concentration of 1 μM. Rates shown on the graph are nmols O2 consumed/min/mg protein. (B) Oxygen consumption by whole E. coli FN102 cells expressing Blastocystis AOX (orange trace) was measured using a high-resolution respirometer compared to E. coli cells not expressing the Blastocystis AOX (brown trace). Oxygen consumption is roughly three times higher in the AOX expressing strain and sensitive to the AOX inhibitor salicylhydroxamic acid (SHAM). Three independent experiments were conducted and a representative data set is presented.