Figure 3.
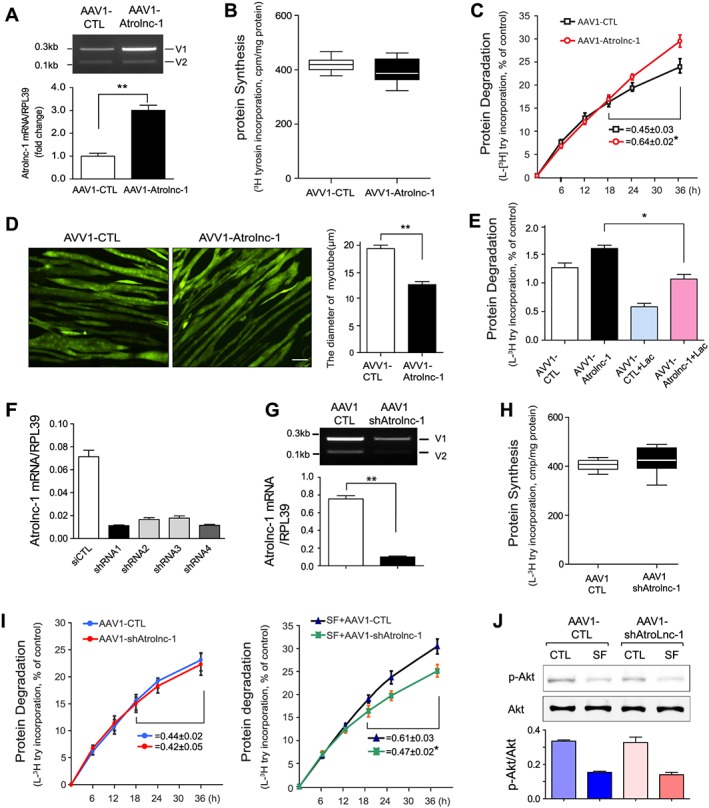
Atrolnc‐1 enhances protein degradation of muscle cells in vitro. (A) qRT‐PCR result shows increased Atrolnc‐1 mRNA levels after the overexpression of Atrolnc‐1 (V1) in C2C12 myotubes (mean ± SEM n = 3, **P < 0.01). V1, Atrolnc‐1 variant 1; V2, Atrolnc‐1 variant 2. (B) The rate of protein synthesis after the overexpression of Atrolnc‐1 in C2C12 myotubes. The rate of protein synthesis was measured from the incorporation of L‐[(3,5)‐3H] tyrosine into cellular proteins (mean ± SEM; n = 6). (C) The rate of protein degradation after the overexpression of Atrolnc‐1 in C2C12 myotubes. Protein degradation was measured by the L‐[(3,5)‐3H]‐tyrosine released into media and plotted as a percentage of total L‐[(3,5)‐3H]‐tyrosine incorporated into cell proteins. The rates of proteolysis were calculated from the linear slopes between 24 and 36 h (mean ± SEM; n = 6, *P < 0.05). (D) C2C12 myotubes with or without Atrolnc‐1 overexpression visualized by infecting adenovirus coding green fluorescent protein (GFP). Scale bar: 20 μm. Graphic presentation (right panel) of the diameter of myotubes calculated from three independent experiments (mean ± SEM, **P < 0.01). (E) C2C12 myotubes with or without Atrolnc‐1 overexpression were treated with a proteasomal inhibitor, lactacystin (Lac). Atrolnc‐1 overexpression‐stimulated proteolysis was largely suppressed by lactacystin (mean ± SEM, n = 6, *P < 0.05). (F) qRT‐PCR result shows Atrolnc‐1 mRNA levels were reduced by four different short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) against Atrolnc‐1. (G) Agarose gel electrophoresis and the graph (low panel) demonstrated that the Atrolnc‐1 mRNA level was reduced by ~90% in C2C12 myotubes transfected with AAV1‐shAtrolnc‐1. (H) The rate of protein synthesis after the knockdown of Atrolnc‐1 in C2C12 myotubes (mean ± SEM; n = 6). (I) The rate of protein degradation after the knockdown of Atrolnc‐1 in C2C12 myotubes cultured with (left) or without (right) serum. At 48 h after transfection, myotubes with or without Atrolnc‐1 knockdown were switched to serum‐free (SF) medium for 36 h. The rates of proteolysis were calculated from the linear slopes between 24 and 36 h (mean ± SEM, n = 6 per group, *P < 0.05). (J) The level of p‐Akt stays unchanged in myotubes with Atrolnc‐1 knockdown when treated with serum depletion (SF).
