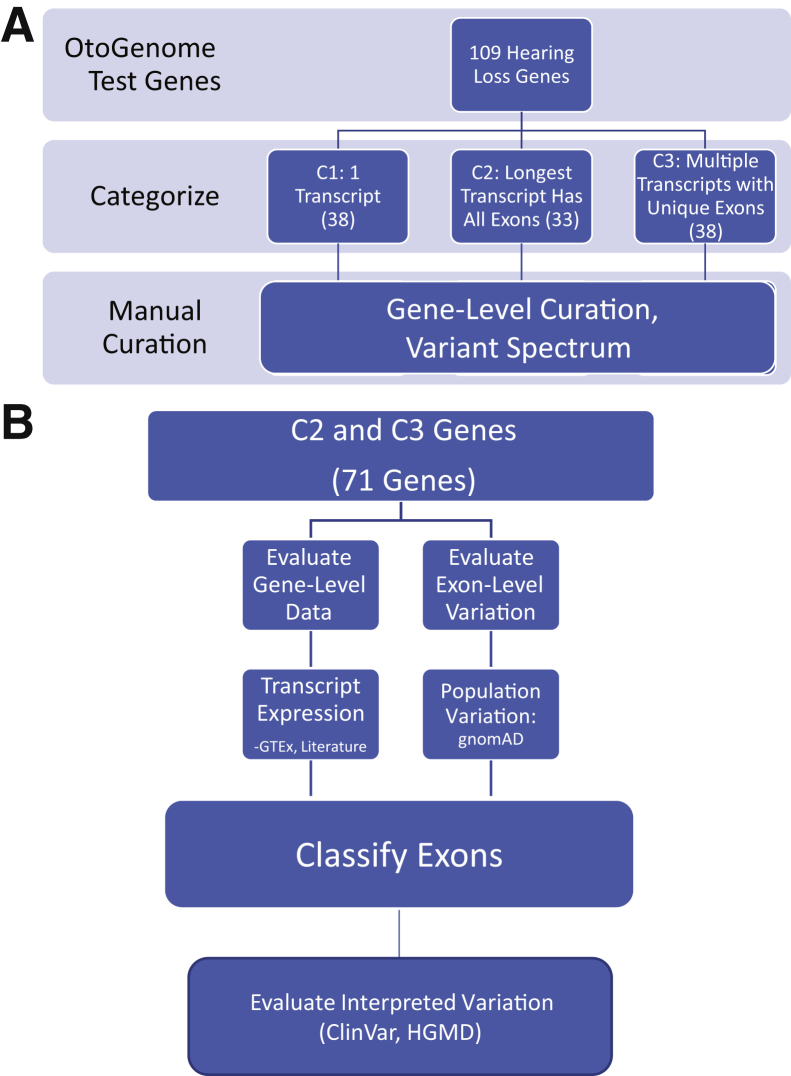
Figure 1.
A: Transcript curation workflow: 109 hearing loss–associated genes, predominantly from the OtoGenome test (GTR000509148.7), were categorized. Genes were divided into three categories using National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) reference sequence transcripts. Category 1 (C1) contained genes that had a single transcript; category 2 (C2) genes had multiple transcripts, but the longest transcript encompassed all exons; and category 3 (C3) genes had multiple transcripts with unique exons. B: Category 2 and 3 curation process: category 2 and 3 genes were manually curated. Exon-specific expression data were obtained from the Genotype-Tissue Expression Project (GTEx). Literature searches were performed for information about functional domains; additional expression data, such as tissue-specific transcript expression; and temporal expression. To evaluate population variation, loss-of-function variants were obtained from the Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD). To evaluate interpreted variation, likely pathogenic/pathogenic variants were retrieved from our internal database (also in ClinVar), and ClinVar and disease-causing mutation variants were obtained from the Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD).