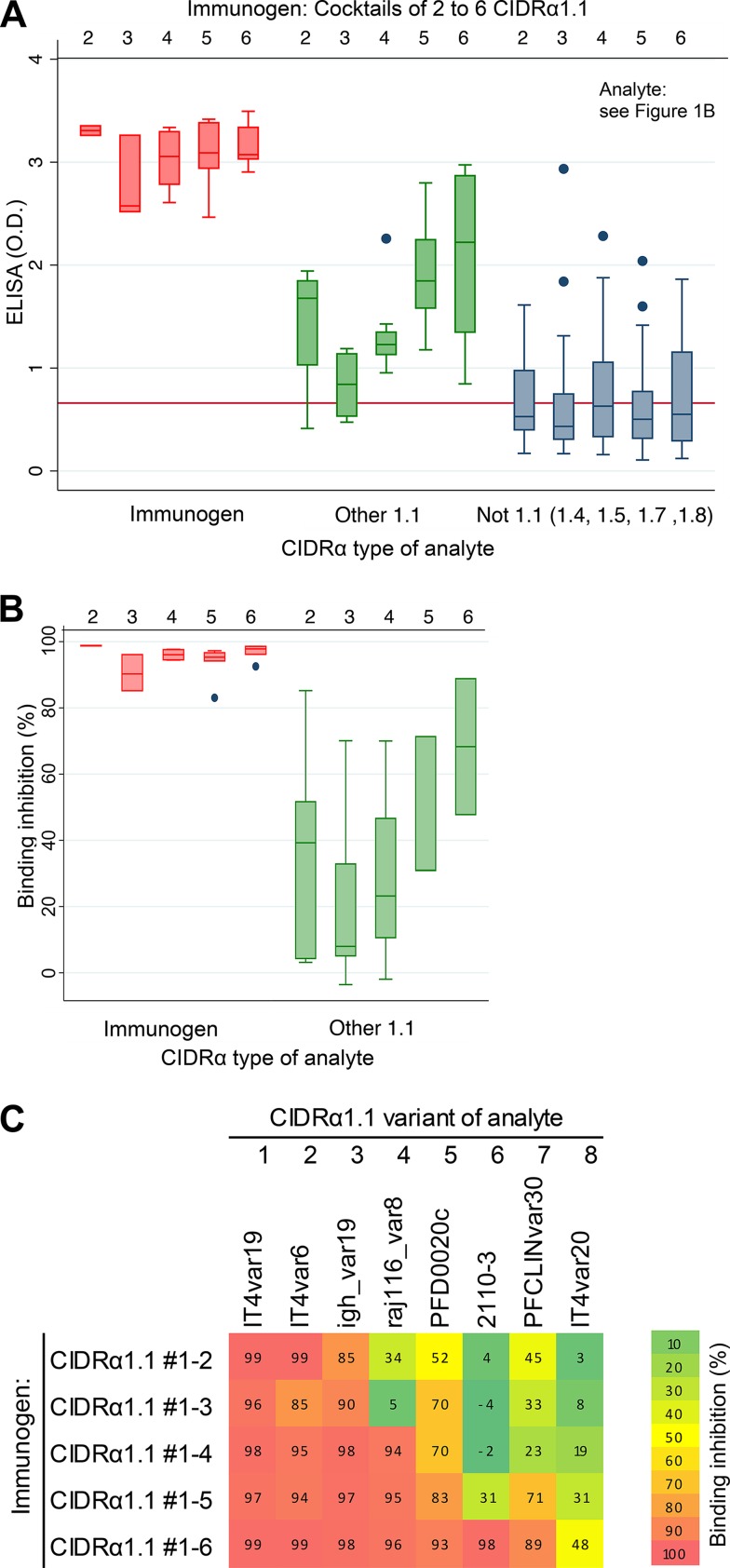
FIG 5.
Reactivity (A) and EPCR binding inhibition (B) of IgG from animals immunized with protein cocktails containing an increasing number of CIDRα1.1 domains, as indicated. Two rats were immunized per antigen cocktail containing between two and six CIDRα1.1 domains (upper horizontal numbering). Antibody reactivity was measured against 31 recombinant CIDRα1 domains (marked E in Fig. 1B): CIDRα1.1 domains present in the immunogen cocktail (immunogen), CIDRα1.1 domains not present on the cocktail (other 1.1), and CIDRα1 domains of subtypes 1.4 to 1.8 (not 1.1). IgG level was measured by ELISA (as optical density [OD]). Box plots show median reactivity with 25th and 75th percentiles and upper and lower adjacent values. For these assays, His-tagged CIDRα1 domains were used both for immunization and for the ELISAs, and plasma was depleted for His-IgG prior to ELISAs. Red lines on left panels indicate levels of residual anti-His-IgG in the plasma. (C) Association between the ability of plasma to inhibit EPCR binding of a given CIDRα1 domain (percent binding inhibition, according to the color map) and the number of CIDRα1.1 domains present in the immunogen cocktail. The eight recombinant CIDRα1.1 domains used for binding inhibition experiments are listed above the heat map, and the composition of immunogen cocktails containing between two and six of these CIDRα1.1 domains is indicated to the left of the panel. The heat map indicates that the rats immunized with six CIDRα1 domains elicited binding-inhibitory IgG against domains 7 and 8 not present in the immunogen.