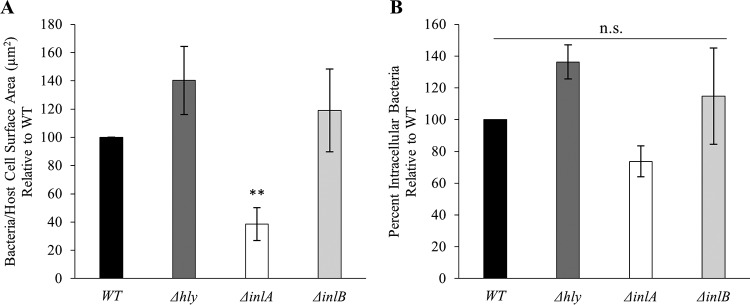
FIG 6.
Role of LLO, InlA, and InlB in L. monocytogenes invasion of human cytotrophoblasts. BeWo cells were infected with WT, LLO-deficient (Δhly), InlA-deficient (ΔinlA), or InlB-deficient (ΔinlB) bacteria (106 bacteria/well) for 30 min at 37°C. The cells were washed, fixed, and labeled with fluorescent antibodies and DAPI. (A) The bacterial association efficiency was calculated as the number of cell-associated bacteria per unit surface area (μm2). The average association for the WT strain before normalization was 0.0015 bacteria/μm2. (B) The bacterial internalization efficiency was measured as the percentage of intracellular bacteria. The average internalization for the WT strain before normalization was 13.82%. The average number of WT bacteria counted per experimental condition was 5,000, with a minimum count of 100 bacteria being required for any mutant with reduced association efficiency. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM relative to the WT (n ≥ 3). Statistical analyses compared each strain to the WT strain and were performed on raw data before normalization (*, P < 0.01; **, P < 0.001; n.s., nonsignificant).