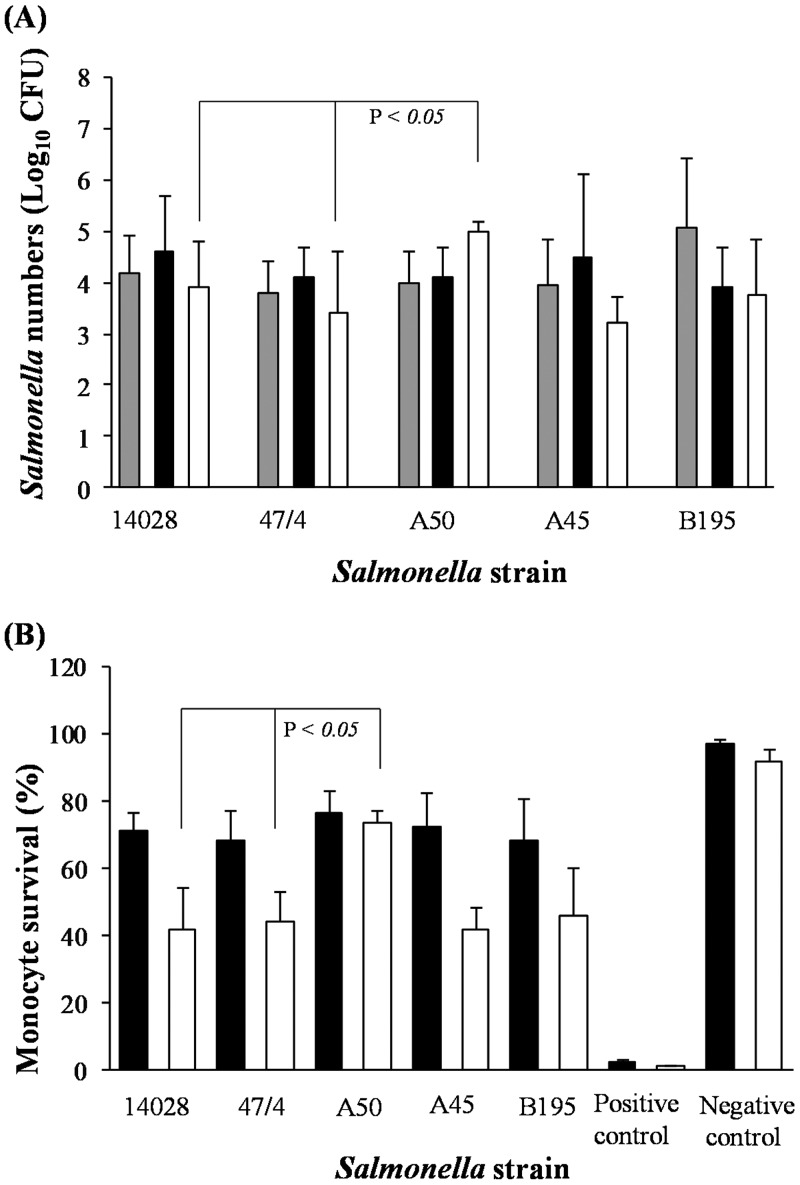
FIG 1.
Salmonella bacterial numbers and human monocyte survival are increased following S. Choleraesuis A50 infection in comparison to S. Typhimurium infection. (A) Numbers of viable CFU of S. Choleraesuis (A50, A45, and B195) and S. Typhimurium (14028 and 4/74) recovered from monocytes at 2, 6, and 24 h p.i. (B) Monocyte viability was measured by propidium iodide uptake and FACS analyses following infection with S. Choleraesuis or S. Typhimurium strains after 6 and 24 h. Monocyte viability was compared with that of negative controls (uninfected monocytes cultured in medium for the same time period) and positive controls (monocytes immersed in ice-cold [−20°C] methanol for 30 min). Error bars represent standard deviations from the mean, and linkage bars at the top of the graph indicate significant differences (P = 0.05). Results shown are mean values calculated from triplicate experiments performed on five separate occasions. Gray bars, 2 h p.i.; black bars, 6 h p.i.; white bars, 24 h p.i.