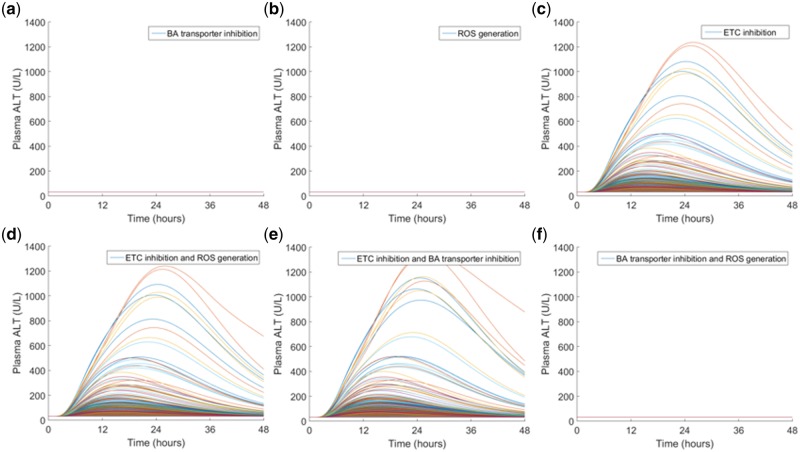
Figure 4.
Qualitative sensitivity analysis based on toxicity mechanisms in rat SimPops. A single dose of 500 mg/kg CKA was simulated in rat SimPops with a single mechanism (top row) or combination of two DILI mechanisms (bottom row). (A) bile acid (BA) transporter inhibition only, (B) reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation only, (C) mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC) inhibition only, (D) ETC inhibition + ROS generation, (E) ETC inhibition + BA transporter inhibition, (F) BA transporter inhibition + ROS generation. Simulations with a single DILI mechanism (top row) suggest that ETC inhibition is the main contributor to CKA-mediated rat hepatotoxicity. When two DILI mechanisms are combined, ETC inhibition and BA transporter inhibition together produce a greater peak plasma alanine transaminase (ALT), suggesting BA transporter inhibition as the secondary contributor to hepatotoxicity. Qualitative results are supported by multiple regression analysis results shown in Supplementary Table 2.