Figure 6.
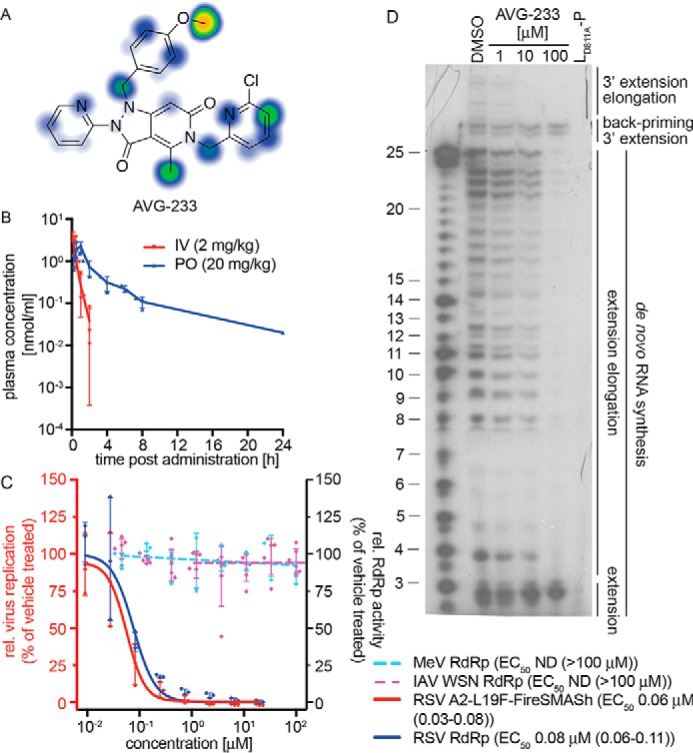
PK profiling and mechanistic assessment of the AVG-233 lead. A, metabolic stability predictions for AVG-233 using SMARTCyp. B, single-dose PK testing of AVG-233 in mice. Animals (three per group) were dosed with AVG-233 intravenously (IV) or orally (PO) at the indicated dose levels. Plasma samples were prepared at the indicated time points and analyzed by LC/MS/MS. C, bioactivity testing of AVG-233 against RSV (red y axis) and RSV–, MeV–, or IAV-WSN–derived minigenome assays (blue y axis). Where applicable, four-parameter variable slope regression models and active concentrations are shown. D, in vitro RSV RdRp activity assay as described in Fig. 4C. The lead compound AVG-233 blocks 3′ RNA extension elongation but does not interfere with 3′ RNA extension by up to three nucleotides after de novo initiation from the promoter or back-priming. IAV-WSN RdRp values in C show means of six biological repeats. Symbols in B–D represent individual biological repeats (n = 3 each); error bars, S.D. IAV-WSN RdRp activity in C was determined in six biological repeats.
