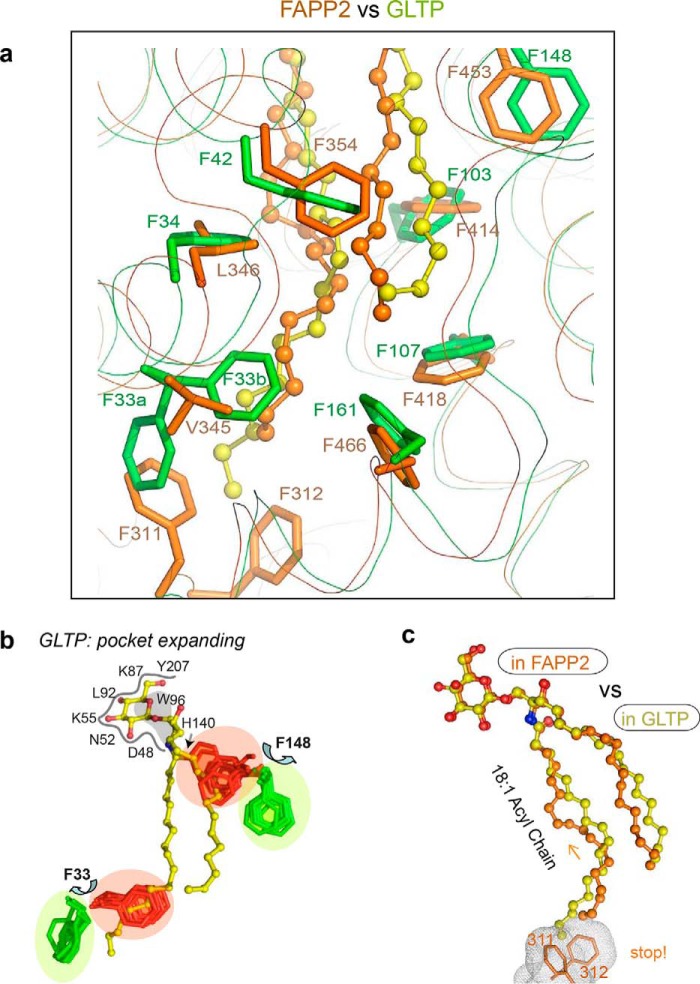
Figure 8.
Location of Phe and FF motifs in the hydrophobic pocket of FAPP2–GLTPH versus GLTP. a, superposition of FAPP2–GLTPH (orange) with GLTP (green) indicating five coinciding Phe positions in the hydrophobic pockets of both proteins but differently located FF motifs (Phe311–Phe312 in FAPP2 versus Phe33-Phe34 in GLTP; for details, see the text). b, two Phe conformations, the open-door (green) and closed-door (red), identified in human GLTP for Phe33 and Phe148 residues via superposition of all available GLTP structures. Phe functionality as doors for Phe33 and Phe148 regulates acyl and sphingosine chain access to the hydrophobic pocket of GLTP. c, 18:1-Acyl chain adaptation within the hydrophobic pockets of FAPP2–GLTPH (versus the pocket of GLTP) depicting the clashing role of FF motif that seals the bottom of the hydrophobic pocket in FAPP2.