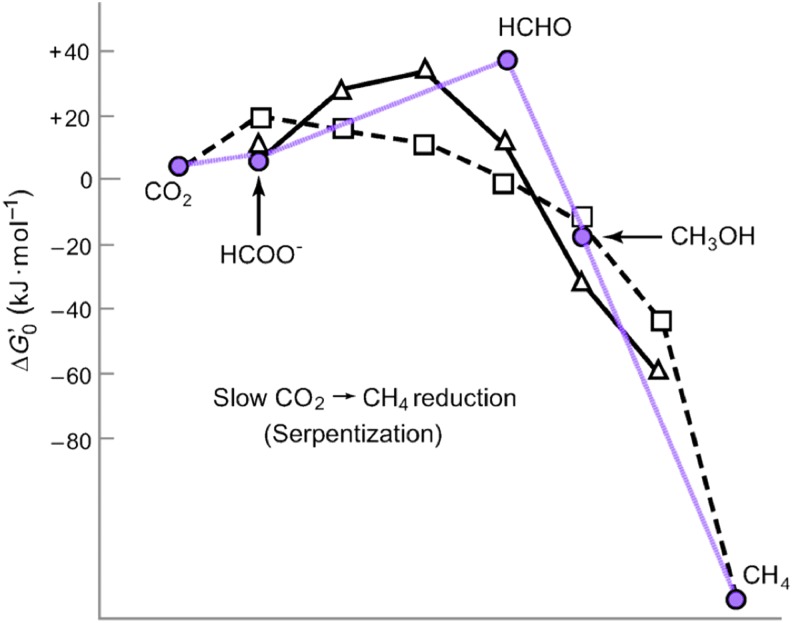
FIG. 4.
Free-energy profile of a hydrothermal pathway (in purple) to methane (Seewald et al., 2006) is contrasted with the reduction profiles of the acetogenic bacteria (triangles) and methanogenic archaea (squares); both biological mechanisms use the acetyl coenzyme-A pathway. We can think of the geochemical pathway as a chemical siphon while the much more rapid biochemical pathways are driven by chemiosmosis over the intermediates formate and formaldehyde (or the formyl group). Adapted from Maden (2000).