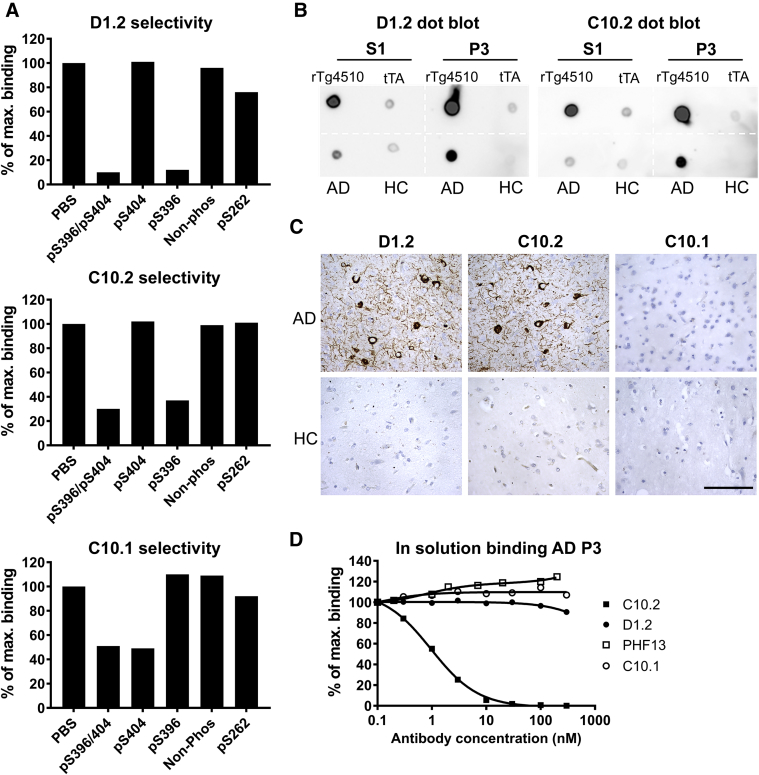
Fig. 2.
Antibody selectivity toward pS396 or pS404 tau (386–408) peptides and disease material. (A) Antibodies were mixed with the indicated peptides and screened for binding on tau (386–408)-pS396/pS404–coated MSD plates. Data presented as percentage binding in relation to PBS control incubation. Both D1.2 and C10.2 bind to tau phosphorylated at S396 but not to nonphosphorylated or S404-phosphorylated tau, whereas C10.1 requires phosphorylation of S404 for binding but not S396. (B) Dot blot demonstrating selective binding by D1.2 and C10.2 to soluble (S1) and sarkosyl-insoluble (P3) fractions isolated from rTg4510 and AD brains compared with tTA littermates and HC brain fractions. (C) Immunohistochemical staining of AD and HC brain sections of frontal cortex. Photomicrographs are representative of three AD and three HC cases, images from a single AD and a single HC case are shown. Scale bar: 50 μm. (D) In-solution binding of antibodies to AD brain. Insoluble P3 tau fraction was mixed with antibodies D1.2, C10.2, C10.1, or PHF13 before binding to C10.2-coated MSD plates. Data are presented as percent P3 binding when preincubated with increasing amounts of antibody in relation to P3 binding without added antibody. At the given antibody concentrations, only C10.2 resulted in a concentration-dependent decrease in binding. Abbreviations: AD, Alzheimer's disease; HC, healthy control; MSD, Meso Scale discovery; PBS, phosphate buffered saline.