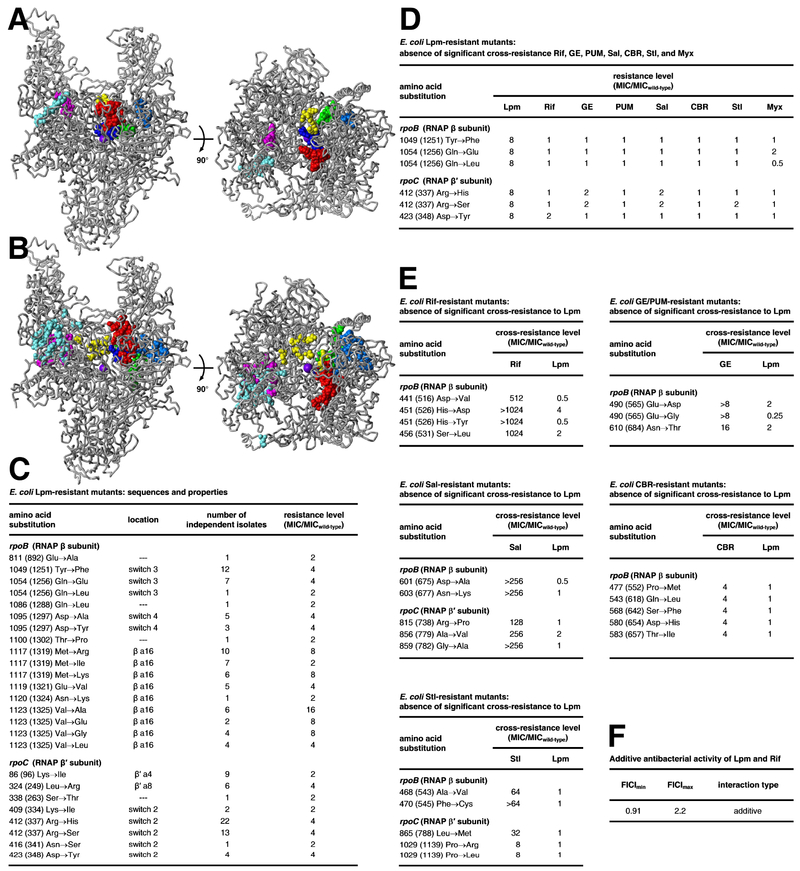
Figure 2. Relationship between binding site and resistance determinant of Lpm and binding sites and resistant determinants of other RNAP inhibitors.
A, Binding positions of Lpm (cyan; Fig. 1), Rif and Sor (red; PDB: 1I6V, PDB: 1YNJ, PDB: 2A68, PDB: 2A69, PDB: 4KN4, PDB: 4KN7, PDB: 4OIR, and PDB: 5UHB), GE and PUM (dark blue; PDB: 4OIN, PDB: 4OIR, and PDB: 5X21), CBR and AAP (light blue; PDB: 4XSY, PDB: 4XSZ, PDB: 4ZH2, PDB: PDB: 4ZH3, PDB: 4ZH4, PDB: 5UHE, and PDB: 5UHF), Sal (green; PDB: 4MEX), Stl (yellow; PDB: 1ZYR), and Myx and SQ (magenta; PDB: 3DXJ, PDB: 3EQL, PDB: 4YFK, PDB: 4YFN, and PDB: 4YFX), mapped onto structure of Mtb RNAP (gray; two orthogonal views; β′MtbSI and σ omitted for clarity). Violet sphere, RNAP active-center Mg2+. B, Resistance determinants of Lpm (cyan; Fig. 2C), Rif and Sor (red; Campbell et al., 2001, 2005), GE and PUM (dark blue; Zhang et al., 2014; Maffioli et al., 2017), CBR703 and AAP (light blue; Lin et al., 2017; Feng et al., 2015; Bae et al., 2015), Sal (green; Degen et al., 2014), Stl (yellow; Tuske et al., 2005; Temiakov et al., 2005), and Myx, Cor, Rip, and SQ (magenta; Mukhopadhyay et al., 2008; Belogurov et al., 2009; Molodtsov et al., 2015) mapped onto structure of Mtb RNAP. C, Sequences and properties of E. coli Lpm-resistant mutants residues numbered as in Mtb RNAP and, in parentheses, as in Escherichia coli RNAP). D, Absence of significant cross-resistance of E. coli Lpm-resistant mutants to Rif, GE, PUM, Sal, CBR, Stl, and Myx. E, Absence of significant cross-resistance of E. coli Rif-, GE/PUM-, Sal-, CBR-, and Stl-resistant mutants to Lpm. F, Additive antibacterial activity of Lpm and Rif. [Resistance and cross-resistance levels for Lpm-, CBR-, and Stl-resistant mutants are from strains having the mutant RNAP subunit gene on a plasmid and the corresponding wild-type RNAP subunit gene on the chromosome (merodiploid strains; see Methods). Resistance and cross-resistance levels for Lpm-, CBR-, and Stl-resistant mutants are from strains having the mutant RNAP subunit gene on the chromosome and no corresponding wild-type RNAP subunit gene (non-merodipoid strains; see Methods). Resistance and cross-resistance levels are expected to be lower for merodiploid strains than for non-merodiploid strains.] See also Fig. S5.