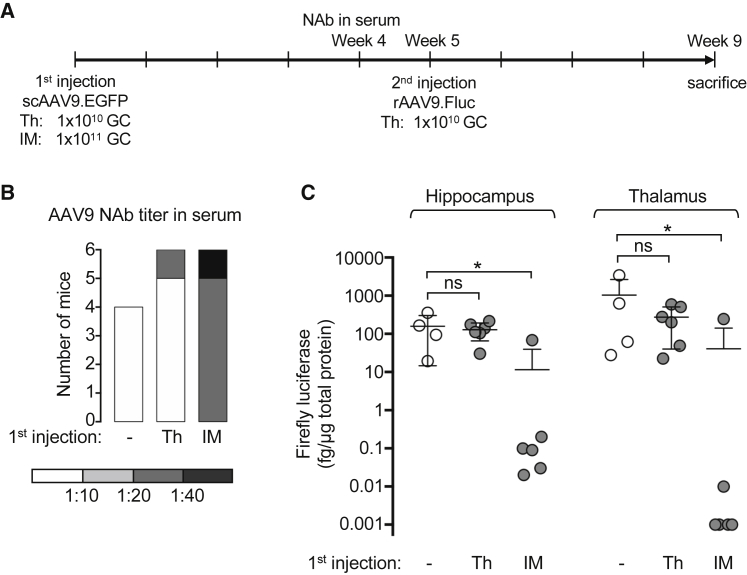
Figure 3.
Pre-immunization with rAAV9 by IM Injection in Mice Compromises CNS Transduction by a Following Brain rAAV9 Delivery
(A) Experimental workflow. Wild-type C57BL/6 mice (male, 6–8 weeks old) received either intrathalamus (Th) or intramuscular (IM) delivery of scAAV9.EGFP as the first injection. Mice receiving no rAAV served as naive controls. Four weeks later, sera were collected to determine the anti-AAV9 NAb titer. One week later, all mice received rAAV9.Fluc by Th delivery. For the mice receiving Th delivery as the first injection, the second Th injection was at the contralateral hemisphere. Four weeks after the second injection, mice were sacrificed for gene expression analysis. GC, Genome copies. (B) Anti-AAV9 NAb titer in the sera collected 4 weeks after the first injection as determined by the in vitro assay. Samples are categorized by the AAV NAb titer that is presented on a gray scale. (C) Quantification of the firefly luciferase expressed in the hippocampus and thalamus of the hemisphere injected with rAAV.Fluc. Each dot represents an individual mouse. The means and SDs of each group (n = 4–6 mice) are shown. *p < 0.05; ns, not significant by Dunn’s test corrected for multiple comparisons within each tissue group.