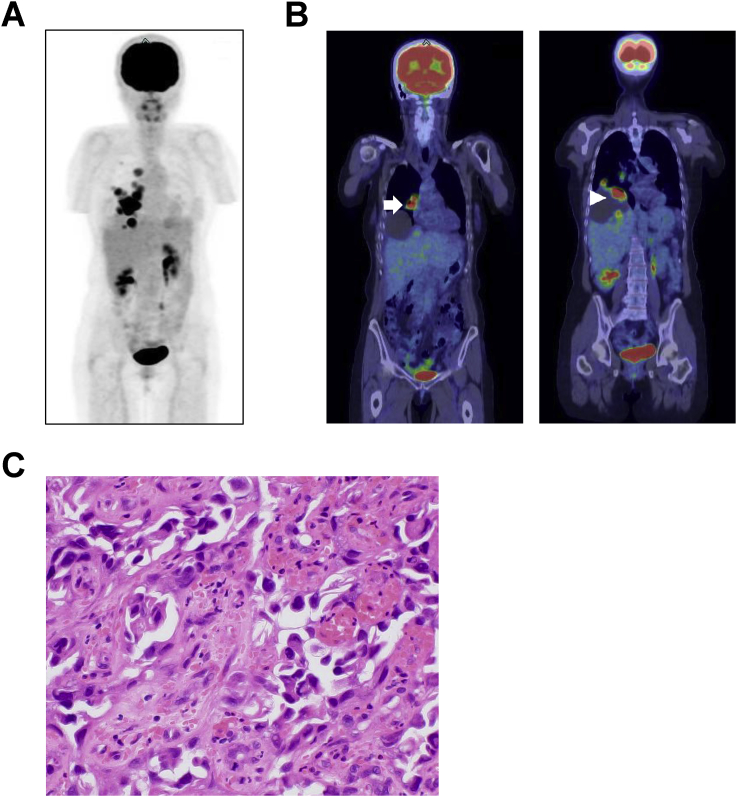
Fig. 1.
Clinical and biopsy images of the patient. (A) PET maximum intensity projection image at the first visit. Abnormal fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake is observed in the right chest or upper abdomen. The kidneys, urinary bladder, and part of the left ureter are also imaged in the abdomen. (B) Coronal PET/CT images identifying a mass in the right lung with FDG accumulation (left panel; arrow) and a cystic liver lesion (right panel). Uptake is seen in the cystic lesion (arrowhead). (C) Histopathological biopsy image: atypical cells with large nuclei and amphophilic cytoplasm proliferating in a hobnail pattern. Original magnification: ×200.