Figure 9. Inverse complementation assay.
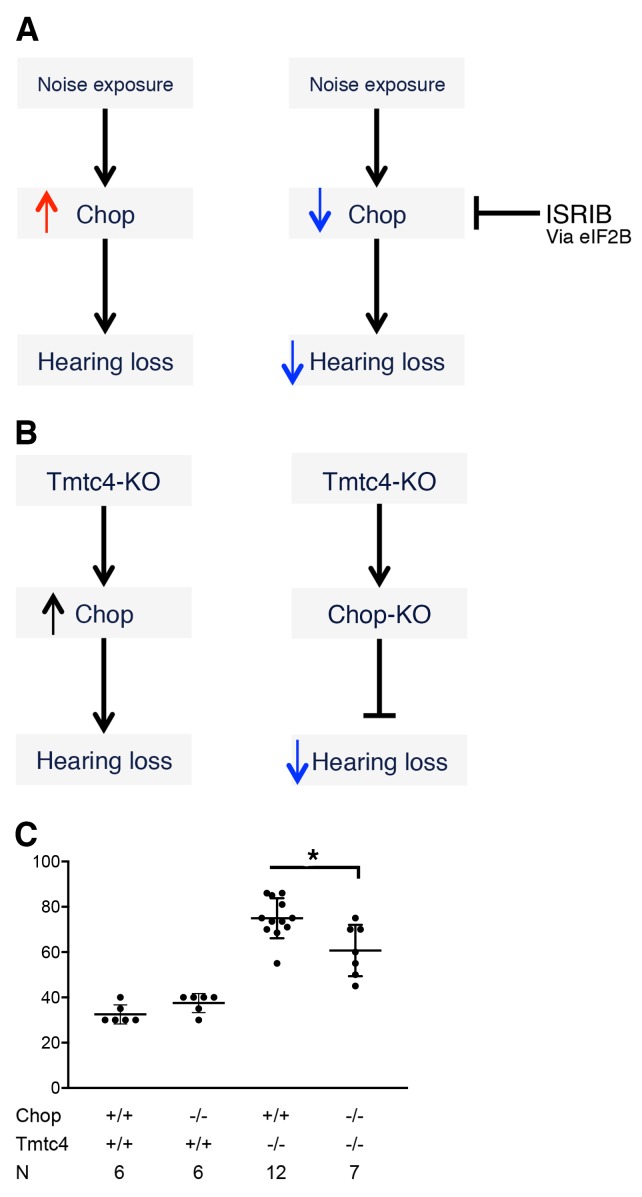
(A) As demonstrated in Figure 8, noise exposure induces expression of the proapoptotic UPR modulator Chop, and pharmacologic inhibition of Chop expression with ISRIB via ATF4 attenuates NIHL. (B) In the genetic model of Tmtc4 deficiency, Tmtc4-KO cochlea demonstrate upregulation of Chop. In an inverse complementation model, we generated double KO mice with both Tmtc4 and Chop deficiency and hypothesized that prevention of Chop expression would attenuate progressive postnatal hearing loss. (C) ABR thresholds were measured for mice of the indicated genotypes for Tmtc4 and Chop. Tmtc4–/– mice were all tested at P19; Tmtc4+/+ mice were all tested at P39 to ensure no long-term hearing loss associated with Chop deficiency alone. Tmtc4–/– mice showed elevated ABR thresholds compared with all Tmtc4+/+ mice; among the Tmtc4–/– mice, Chop–/– genotype was associated with improved hearing compared with Chop+/+ mice. *P < 0.01 by unpaired 2-tailed t test. Data represent mean and SD.