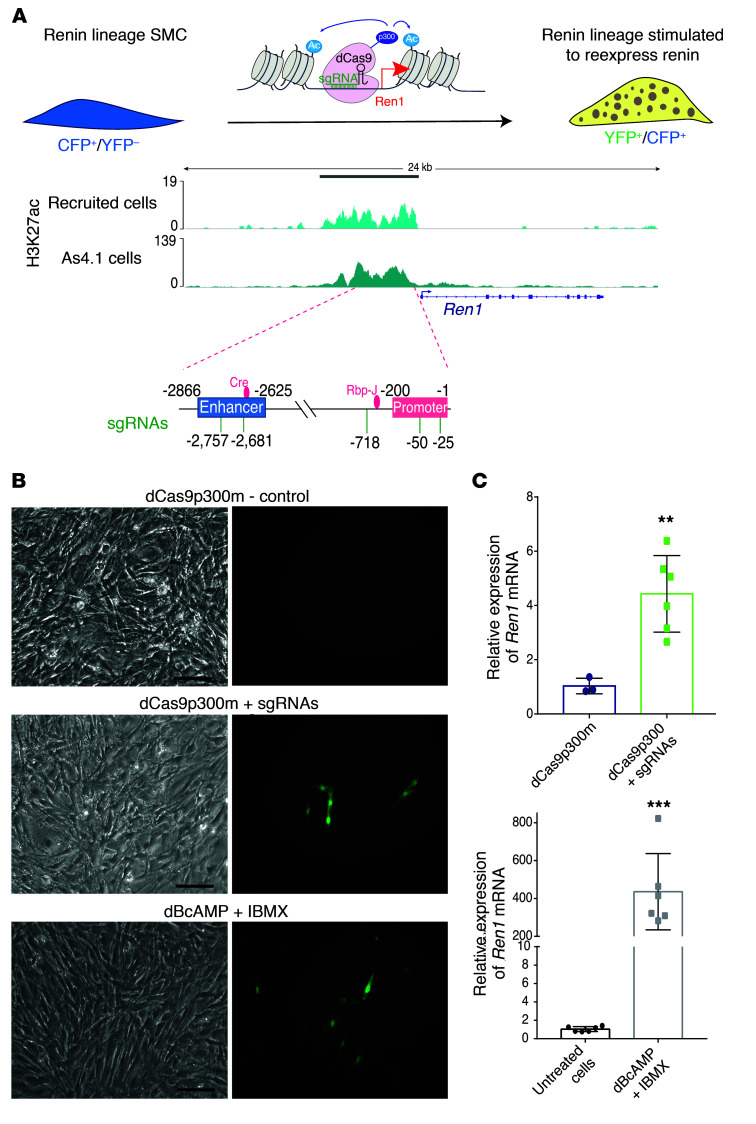
Figure 5. The molecular memory of the renin phenotype resides within the renin super-enhancer.
(A) In vitro model to study the molecular memory of the renin cell phenotype. The immortalized SMCCFP/YFP cell line derived from the mouse kidney constitutively expresses the renin lineage marker CFP and can be induced to express renin (and YFP) upon stimulation. The nuclease-null dCas9 protein is fused to the catalytic core of p300 and catalyzes the acetylation of H3K27. The renin locus showing the renin super-enhancer region in renin cells (indicated by the grey bar on top) previously characterized H3K27ac signal in renin cells. The schematic shows the locations of the sgRNAs used to target the SE region of renin. (B) Bright field images (left panels) of corresponding fluorescent images (right panels). Top, no YFP+ cells were observed in the controls where cells were transfected with a plasmid containing dCas9 bearing mutated p300. Middle, SMCCFP/YFP expressing YFP 72 hours after transfection with a plasmid containing the sequence for the dCas9p300 core and 5 sgRNAs targeted to the renin super-enhancer. Bottom, YFP expression in SMCCFP/YFP treated with 1 mM dB-cAMP and 0.1 mM IBMX for 72 hours to stimulate renin expression. Scale bars: 10 μm. (C) Relative mRNA expression of Ren1, determined by qRT-PCR. The levels of renin expression increased 4.37 to 477 times in response to dCas9p300 + sgRNAs (n = 6) or to exogenous cAMP (n = 6), respectively, versus control samples (dCas9p300-mutated and untreated cells, n = 3 and n = 6, respectively). Data are mean ± SD. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0. 001, by unpaired, 2-sided Student’s t test.