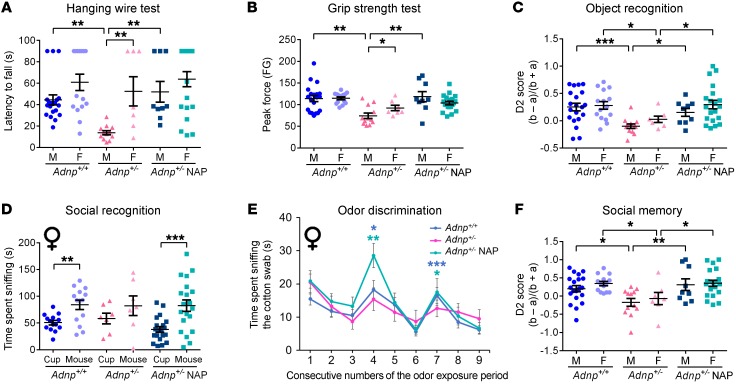
Figure 7. Influence of the Adnp genotype on motor, memory, and social aspects, all of which improve with NAP treatment.
A 2-way ANOVA or 2-way, repeated-measures ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test was performed (males: Adnp+/+ n = 20, Adnp+/– n = 12, Adnp+/– NAP, n = 9; females: Adnp+/+ n = 14–15, Adnp+/– n = 7, Adnp+/– NAP, n = 20). (A) To assess neuromuscular ability, the latency (seconds) to fall off an inverted cage lid was determined by a hanging wire test. For males, a main group effect was found [F(3,49) = 8.186, P < 0.001], with significant differences between Adnp+/+ and Adnp+/– mice and NAP- versus vehicle-treated Adnp+/– mice (**P < 0.01, 2-way ANOVA). Sex differences were found among Adnp+/– mice (**P < 0.01, Mann-Whitney U test). (B) To assess forelimb grip strength, peak grip force was evaluated. For males, a main group effect was found [F(3,49) = 6.154, P = 0.001], with significant differences between Adnp+/+ and Adnp+/– mice and NAP- versus vehicle-treated Adnp+/– mice (**P < 0.01, 2-way ANOVA). Sex differences were found in Adnp+/– mice (*P < 0.05, Mann-Whitney U test). FG, grip force. (C) For object recognition assessment, a main genotype effect in males [F(1,49) = 7.037, P = 0.011] and a main interaction effect in females [F(1,56) = 5.386, P = 0.024] were found. In both sexes, significant differences between Adnp+/+ and Adnp+/– mice and NAP- versus vehicle-treated Adnp+/– mice were observed (*P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001). The discrimination 2 score (D2) was determined using the following equation: D2 = (b – a)/(b + a), where a = time spent exploring the familiar object, and b = time spent exploring the novel object. (D) For social recognition among female mice, a main effect for the sniffed item was found [F(1,56) = 30.447, P < 0.001], with significant differences between the time spent sniffing the cup and the mouse for Adnp+/+ mice (**P < 0.01) and NAP-treated Adnp+/– mice (***P < 0.001 vs. cup). (E) Female Adnp+/– mice exhibited impaired olfactory function, which was restored by NAP treatment. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 versus previous sniffing (novel vs. familiar odor), by paired Student’s t test (Adnp+/+ n = 11, Adnp+/– n = 5, Adnp+/– NAP n = 15). (F) Social memory was assessed. For males, main treatment [F(1,49) = 4.573, P = 0.037] and interaction [F(1,49) = 4.473, P = 0.040] effects were found. For females, a significant main interaction effect [F(1,56) = 4.463, P = 0.039] was found. Among both sexes, significant differences between Adnp+/+ and Adnp+/– mice and NAP- versus vehicle-treated Adnp+/– mice were observed (*P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01). (A–C and F) Adnp+/+ data are reshown in Supplemental Figure 14, A–D. (D and E) Adnp+/+ data are reshown in Supplemental Figure 14, E and G.