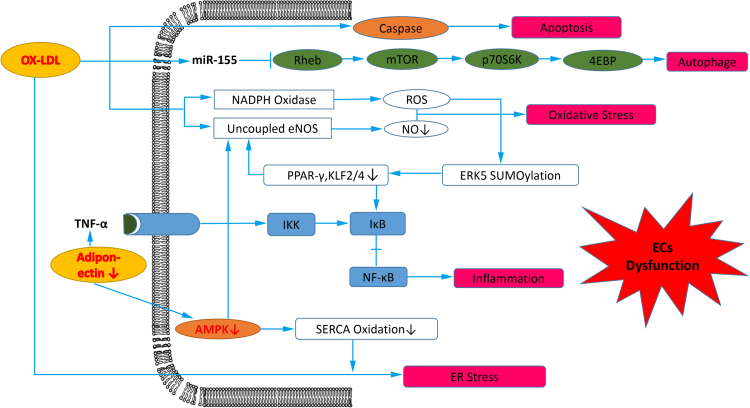
Fig. 2.
Downstream products of ROS promote endothelial cells (ECs) dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Ox-LDL induces ECs apoptosis via caspase dependent or independent pathway, and induces ECs autophage by repressing the Rheb-mediated mTOR/P70S6kinase/4EBP signaling pathway through increased miR-155 expression. Furthermore, ox-LDL induces oxidative stress in ECs through agumented NADPH oxidase and uncoupled eNOS. ERK5 SUMOylation induced by ROS leads to transrepression of atheroprotective genes PPARγ and KLF2/4-mediated eNOS expression, both of which increase NF-κB activation. Decreased adiponectin increase NF-κB activation, and decreased AMPK increase ER stress induced by ox-LDL via enhanced SERCA oxidation.