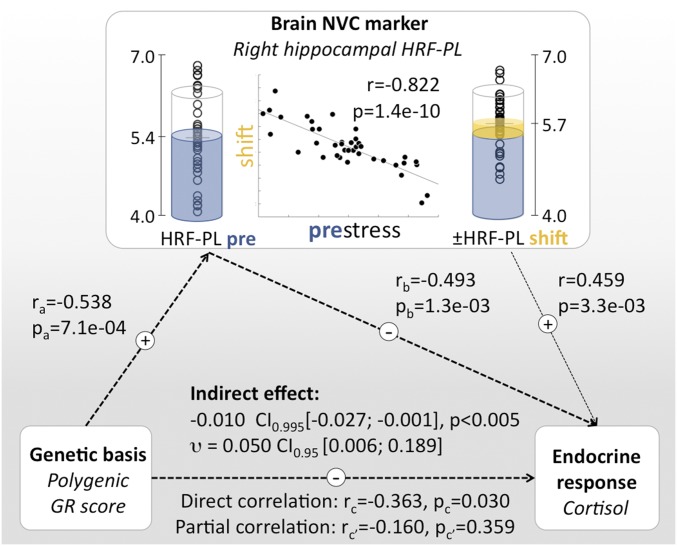
Fig. 6.
Integrating polygenic differences in the transcriptional response to GR activation (PGS), HC HRF-PL, and the endocrine response. There are significant correlational links between the PGS, stress-induced cortisol release, and HC HRF-PL values. Note the close inverse relationship between HC prestress HRF-PL and stress-induced HRF-PL shift [central scatter plot and prestress/stress condition-specific data points; see also SI Appendix, Fig. S7]. (Left) PGS as static genetic influence. (Center) Baseline HC HRF-PL and stress-induced HRF-PL redistribution. (Right) Endocrine response. Based on the temporal order of observations and known HC functions regarding HPA axis regulation, the degree of a putative mediating role of HRF-PL was probed, revealing a significant indirect effect of HC prestress HRF-PL values. A weaker indirect effect was detected for the HC HRF-PL shift as a mediating variable [−0.006, 95% CI (−0.016; −0.001), P < 0.05; effect size υ: 0.020, 95% CI (0.001; 0.088)].