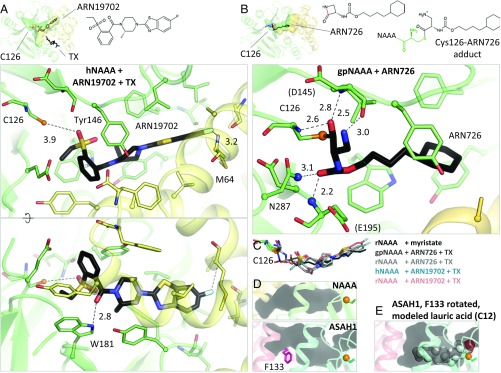
Fig. 4.
NAAA inhibitor complexes. (A) Crystal structure of hNAAA with ARN19702 in presence of TX. Residues forming hydrogen bonds (dashed lines) with the inhibitor are labeled, with interatomic distances (in angstroms). (B) Crystal structure of gpNAAA covalently bound to ARN726. The scissile bond is colored in red in the free inhibitor chemical structure. Nitrogen atoms forming the oxyanion hole are displayed as blue spheres. (C) Comparison of binding orientations of inhibitors and product. (D) In acid ceramidase (ASAH1, PDB ID code 5U7Z), the corresponding cavity is shorter and partially blocked by a phenylalanine side chain (pink). (E) This side chain was reoriented and a lauric acid molecule was manually placed into the ASAH1 cavity.