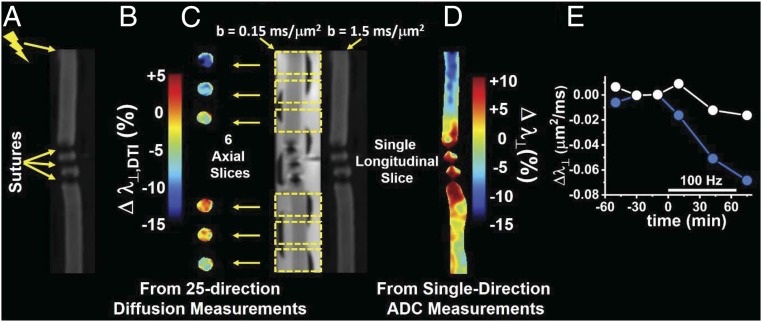
Fig. 8.
Conceptual demonstration of diffusion fMRI to locate AP conduction blockage. (A) The perfused nerve was tied off in the middle by three silk sutures, and stimulation was applied via suction electrode at the proximal end, as indicated, for a period of 60 min at 100-Hz frequency. (B) The diffusion fMRI response is depicted here as the percent change in Δλ⊥ (from DTI analysis of the 25-direction diffusion imaging data acquired in six axial image slices) prestimulation to poststimulation. The positions of the axial slices along the nerve are shown in C. (C) Two DW longitudinal slice images along the length of the nerve with diffusion-encoding gradients applied orthogonal to the axonal fibers with b values of 0.15 and 1.5 ms/μm2. The two DW images are used to generate maps of λ⊥ from this single-diffusion-direction measurement. (D) The diffusion fMRI response Δλ⊥ (percent change) from prestimulus and poststimulus single-direction λ⊥ maps. (E) Time-course average Δλ⊥ for the two slices proximal to the conduction blockage (blue) and the two most distal slices (white).