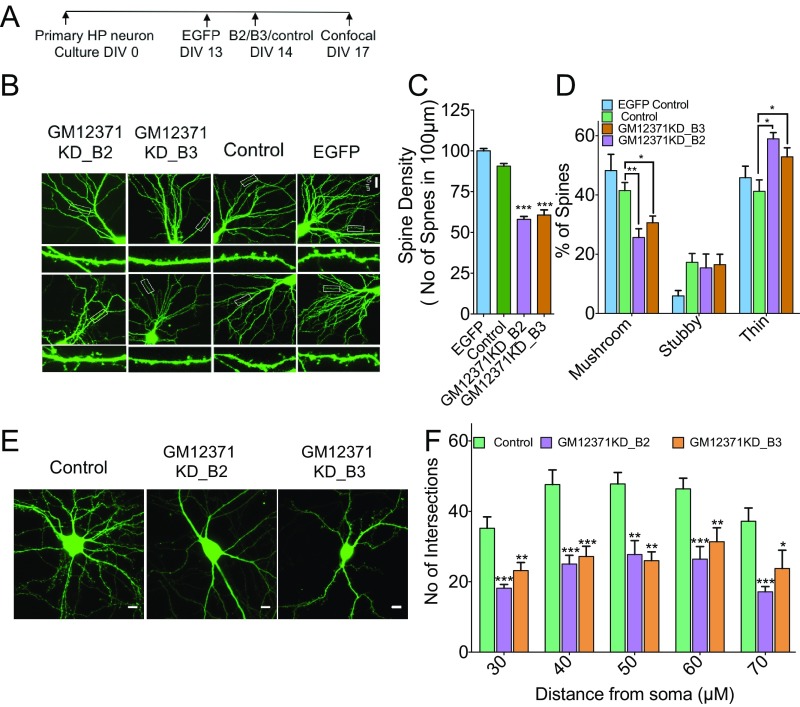
Fig. 2.
GM12371 regulates spine density, spine morphology, and dendritic tree complexity in hippocampal neurons. (A) Experimental outline. (B) Two representative confocal projection images of spines collected at different conditions are shown. (Scale bar, 20 µm.) Two different gapmeRs were used to knock down GM12371. A nontargeting gapmeR was used as control for knockdown. (C) Quantification of total spine density. Bar graphs show number of spines per 100 μm of distal dendrites quantified in EGFP control, control gapmeR, and gapmeR B2 and B3 knockdown neurons. (D) Quantitation of specific changes in spine morphology. Number of neurons analyzed for EGFP control = 20, gapmeR control = 18, gapmeR B2 = 17, gapmeR B3 = 24. (E) Sholl analysis to assess the effect of GM12371 knockdown on dendritic tree complexity. Shown are confocal projection images of EGFP expressing hippocampal neurons following transfection by nontargeting gapmeR (neg control), gapmeR B2 (GM12371 KD_B2), and B3 (GM12371 KD_B3) to specifically knock down GM12371. (Scale bars, 20 μm.) (F) Bar graphs show number of intersections at varying distances from soma. Number of neurons analyzed for gapmeR control = 18, gapmeR B2 = 18, gapmeR B3 = 25. Error bars are SEM, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test.