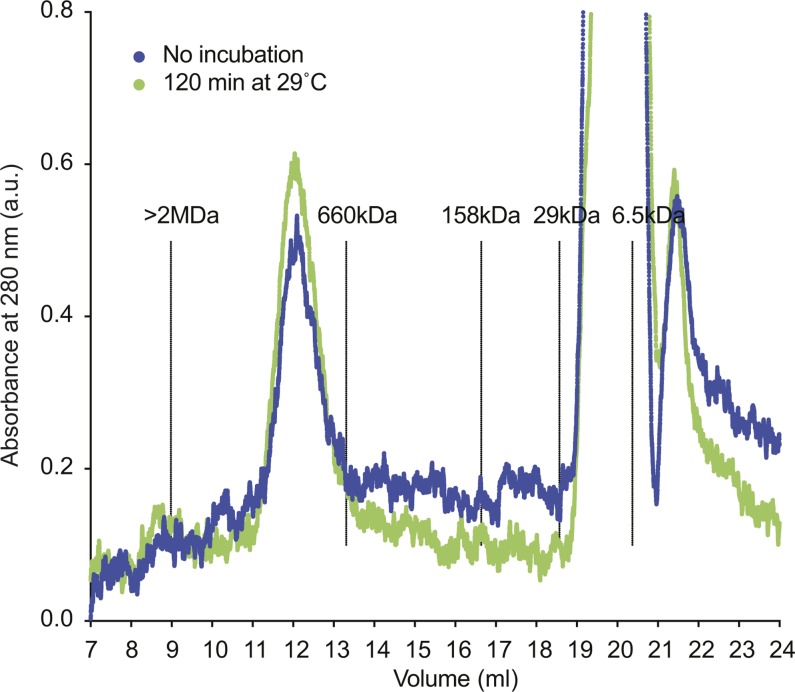
Figure S3. Cohesin retains its oligomeric state during incubation at low ionic strength.
15 pmol of tetrameric cohesin was diluted to 150 nM in cohesin loading buffer (35 mM Tris–HCl pH 7.0, 20 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM MgCl2, 13.3% glycerol, 0.5 mM ATP, 0.003% Tween, 1 mM TCEP) to mimic the conditions of a cohesin loading reaction. The final cohesin concentration was somewhat higher than in a typical loading reaction, which was required to detect the protein in the following analysis. The sample was separated on a Superose 6 Increase 10/300 GL column equilibrated in R buffer (20 mM Tris–HCl pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, 0.5 mM TCEP) or was first incubated at 29°C for 120 min and then separated. In both samples, cohesin eluted at the expected size of the tetrameric complex (compare Fig S1A). At later elution volumes, the absorptions of detergent and ATP become apparent. The positions of the separation peaks of blue dextran (>2 MD), thyroglobulin (660 kD), aldolase (158 kD), carbonic anhydrase (29 kD) and aprotinin (6.5 kD), under the same conditions, are shown as a reference.