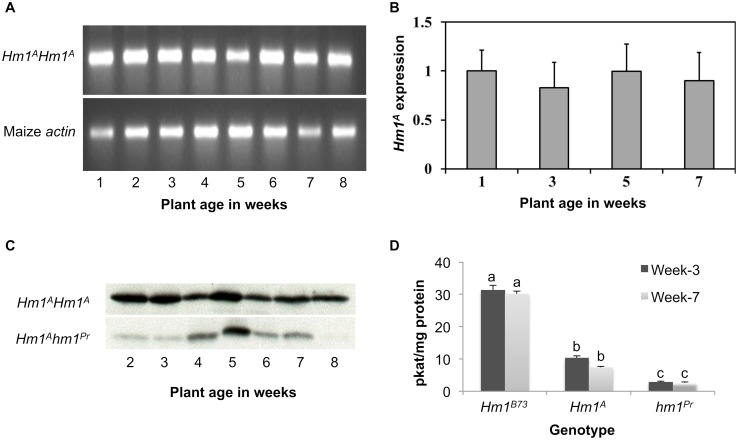
Fig 3. Transcriptional and translational activities of Hm1A during the seedling and mature stages.
(A) Reverse transcription (RT)-PCR assay showing no change in Hm1A accumulation in leaves from week-1 through week-8 after planting. The actin gene was used as a control. (B) Quantitative real time PCR (qRT-PCR) measurements of the expression of Hm1A also demonstrates no change in Hm1A accumulation across the time period when APR is established. (C) Western blots showing that the level or stability of the HM1A protein do not change over time during plant development. Equal amounts of protein were loaded following quantification with the Bradford method. (D) In vitro HC-toxin reductase (HCTR) assays showing that the relative enzymatic activity encoded by Hm1A is less than Hm1B73 but higher than hm1Pr, the null allele. The specific activity of HCTR varies between alleles but not over time between weeks-3 and -7 in any genotype. The HCTR assay was based on the determination via LC-MS/MS of the amount of HC-toxin reduced by leaf protein extracts from the leaves of all genotypes. Different letters indicate significant differences between genotypes (padj < 0.05).