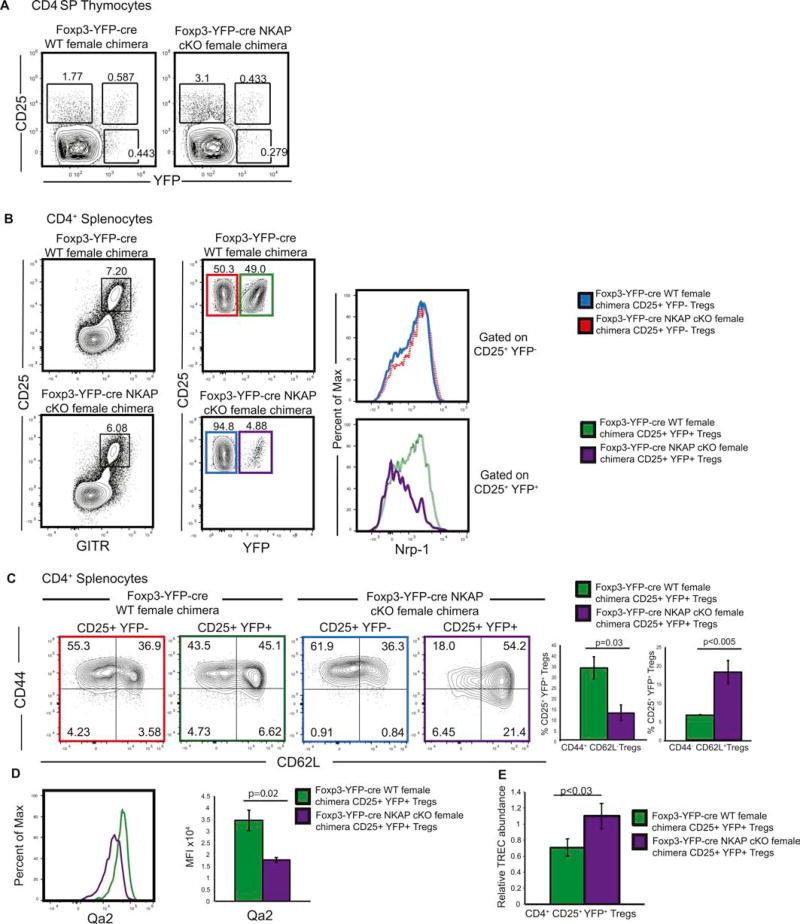
Figure 4. Loss of Tregs as a result of NKAP deficiency is a cell-intrinsic defect.
(A) Analysis of Treg development in Foxp3-YFP-cre NKAP cKO chimeric females and Foxp3-YFP-cre WT chimeric females. Data is representative of 7 independent experiments with 7 mice in each group. (B) Analysis of splenic CD4+ CD25+ GITR+ YFP+ Treg and CD4+ CD25+ GITR+ YFP− Treg frequencies and examination of expression of Nrp-1 in CD4+ CD25+ YFP+ Tregs, and CD4+ CD25+ YFP− Tregs in Foxp3-YFP-cre NKAP cKO chimeric females and Foxp3-YFP-cre WT chimeric females. Data is representative of 6 experiments with 6 mice in each group. (C) Examination of CD44 and CD62L expression in CD4+ CD25+ YFP+ and CD4+ CD25+ YFP− Tregs in Foxp3-YFP-cre WT and Foxp3-YFP-cre NKAP cKO female mice. Use of color to identify samples refers to gated populations in (B). Data is representative from 3 independent experiments with at least 3 mice per group. (D) Examination of Qa2 in CD4+ CD25+ YFP+ Tregs in Foxp3-YFP-cre NKAP cKO chimeric females and Foxp3-YFP-cre WT chimeric females. Use of color to identify samples refers to gated populations in (B). Data is representative from 3 independent experiments with at least 3 mice per group. (E) Analysis of TCR excision circle (TREC) performed on CD4+ CD25+ YFP+ cells sorted, from four pairs of mice, a Foxp3- YFP-cre NKAP cKO female chimeric mouse and a Foxp3-YFP cre WT female chimeric mouse. For the final analysis, DNA from one of the WT mice was chosen as a normalizer and a paired Student’s T test was used to determine significance.