Figure 4. α2δ−1–bound NMDARs contribute to brain injury and neurological deficit caused by MCAO in the brain.
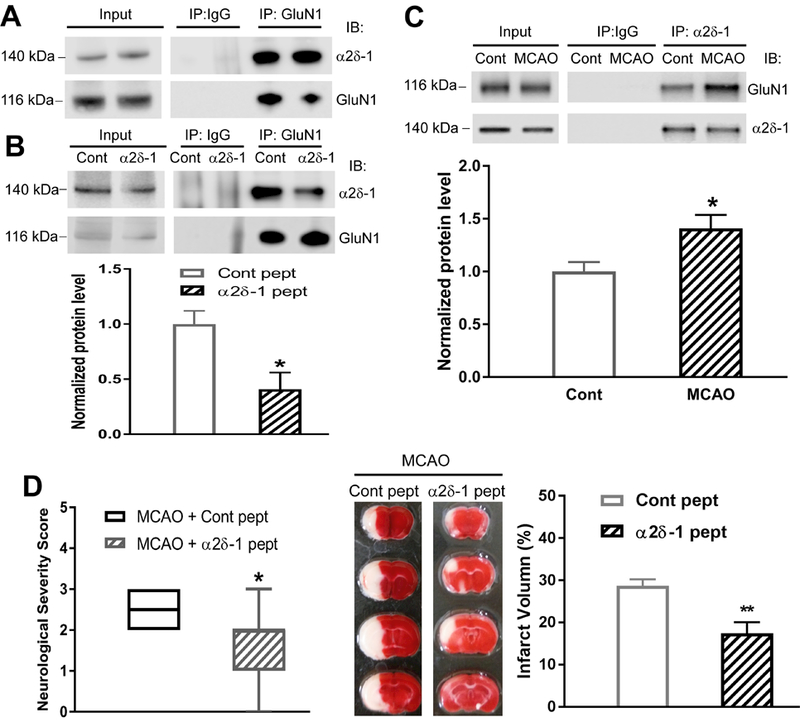
(A) Original co-IP gel images show the interaction between α2δ−1 and GluN1 in two samples from mouse brain tissues. (B) Effect of α2δ−1Tat peptide (1 µM for 60 min) on the α2δ−1–GluN1 protein complex in mouse brain tissues (n = 6 mice per group). (C) Representative gel images and quantification of co-IP analysis show the effect of 15 min of MCAO followed by 2 h of reperfusion on the α2δ−1–GluN1 protein complex level in mouse brain tissues (Cont, sham control; n = 6 samples from 12 mice per group). (D) Neurological severity scores shown in a box-whisker plot (left) and representative TTC staining and quantification (right) of brain infarct volume in MCAO mice treated with α2δ−1Tat peptide or control peptide (both 200 µg/kg, i.p.) at 15 min before MCAO and immediately before reperfusion (n = 8 mice per group). Data are shown as means ± SEM (neurological deficit score data shown as median ± min-max). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 compared with the control peptide-treated or sham control group.
