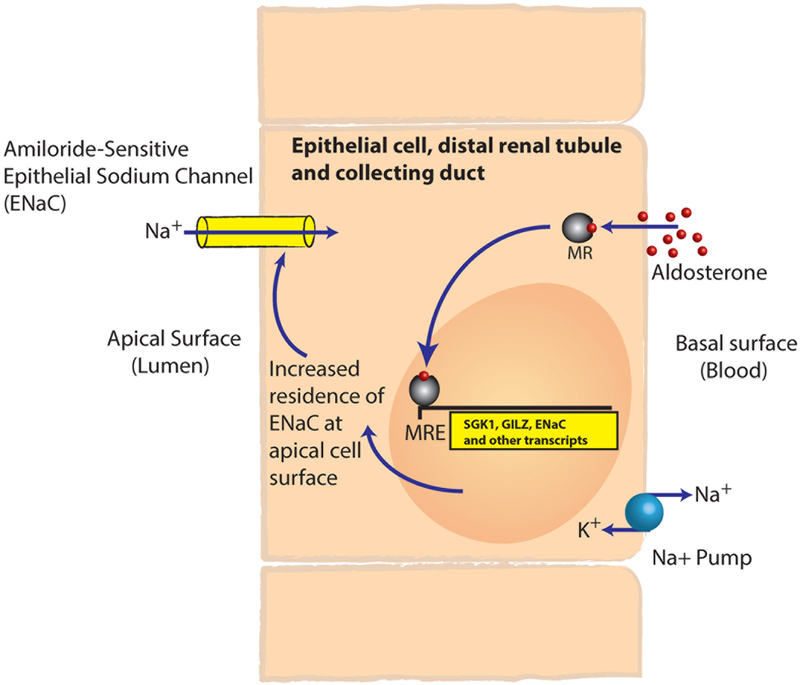
Figure 1.
Illustration of the ligand-activated transcription-factor activity of the mineralocorticoid receptor. The liposoluble steroid hormone aldosterone diffuses into cells and binds to and activates the mineralocorticoid receptor. The mineralocorticoid receptor then dimerizes and translocates to the nucleus, where it binds a hormone-response element and regulates the transcription of target genes. This process regulates the abundance of the amiloride-sensitive epithelial-sodium channel on the apical surface of the epithelial cells in the distal-renal tubule and collecting duct, controlling the final 1-5% of sodium reabsorption. MR, mineralocorticoid receptor; MRE, mineralocorticoid response element; SGK1, serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase; GILZ, glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper; ENaC, amiloride-sensitive epithelial-sodium channel.