Fig. 2.
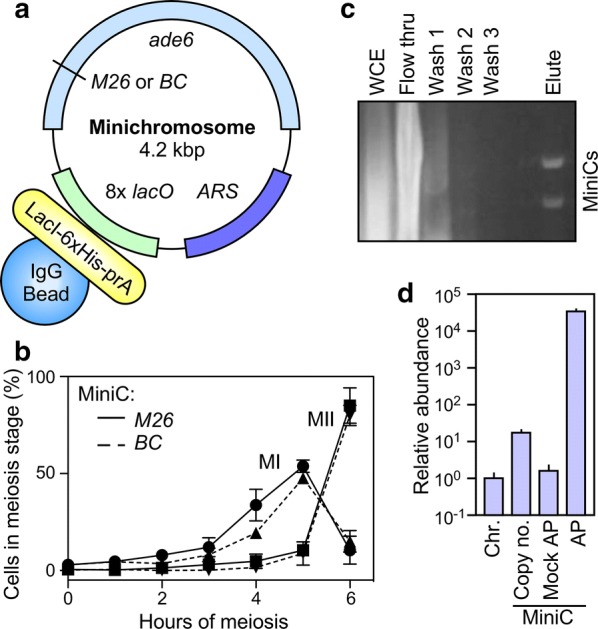
Purification of minichromosomes (MiniCs) from highly synchronous meiosis. a Structure of MiniCs. Recombination hotspot (M26) and basal control (BC) MiniCs contain different alleles of the ade6 gene, a fission yeast origin of replication (ARS) and copies of the LacO DNA site for affinity purification. b Efficiency and synchrony of induced meiosis. Plots show the frequencies of cells undergoing the first meiotic division (MI, 2 nuclei) and having completed the second meiotic division (MII, 3–4 nuclei) in strains harboring the indicated MiniCs. c The indicated samples of chromatin from steps of purification were deproteinized, and their DNAs were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis (WCE, whole-cell extract). d MiniC copy number and degree of enrichment; note log scale. The abundance of ade6 DNA in the chromosome (Chr) or in the MiniC (with chromosomal ade6 deleted) was determined by qPCR, relative to the act1 locus, and those values were normalized relative to single-copy ade6 in the chromosome. Affinity purifications (AP) employed LacI-6xHis-prA; mock AP samples were processed identically, but lacked LacI-6xHis-prA. In this figure and others, plots with error bars are mean ± SD from three or more biological replicates
