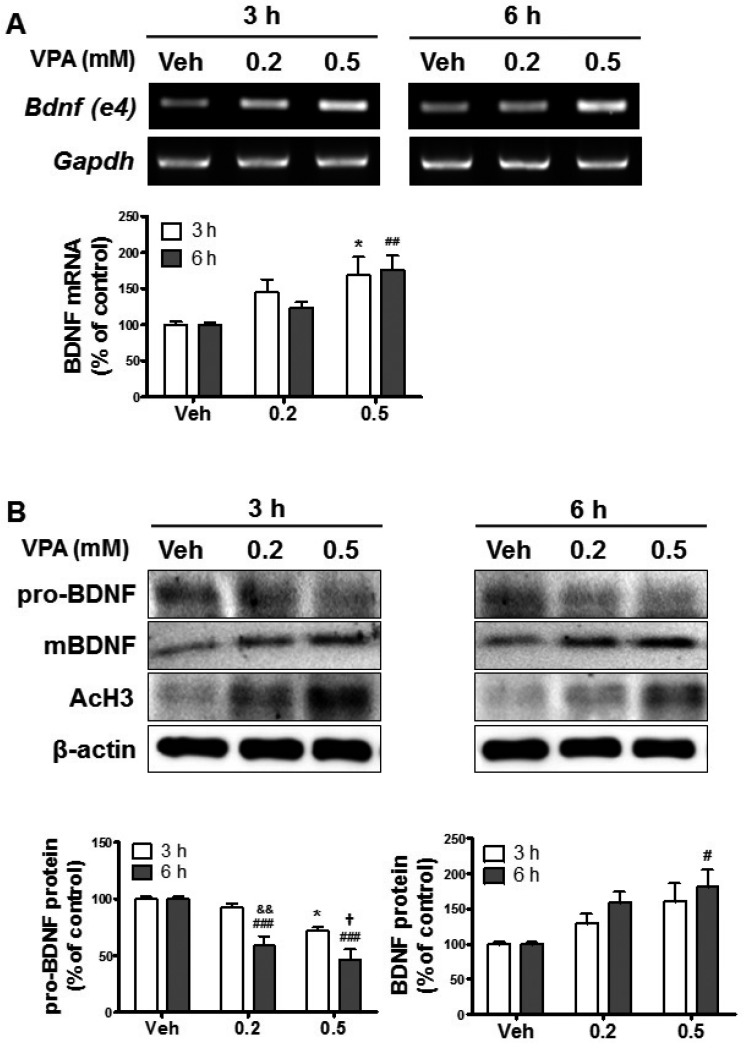
Fig. 1. Valproic acid (VPA)-induced upregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in cultured neural progenitor cells (NPCs).
Neurospheres were cultured from the cortical region of embryonic-day-14.5-old brains and dissociated into single NPCs. The NPCs were exposed to 0.2 or 0.5 mM VPA for 3 or 6 h and then analyzed. (A) The expression of BDNF mRNA was analyzed by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Gapdh was used as a loading control. All data are expressed as mean±standard error of the mean (SEM, n=3). *p<0.05 vs. Vehicle 3 h, and ##p<0.01 vs. Vehicle 6 h [one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by post hoc Tukey's comparisons test]. (B) The expression levels of pro- and mature BDNF protein were analyzed by western blots. Acetylated histone 3 (AcH3) levels were increased by VPA treatment, and β-actin was used as a loading control. All data are expressed as mean±SEM (n=3). *p<0.05 vs. Vehicle 3 h, and #p<0.05 and ###p<0.001 vs. Vehicle 6 h (one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey's comparisons test). &&p<0.01 vs. VPA 0.2 mM 3 h, and †p<0.05 vs. VPA 0.5 mM 3 h (Student's t-test).