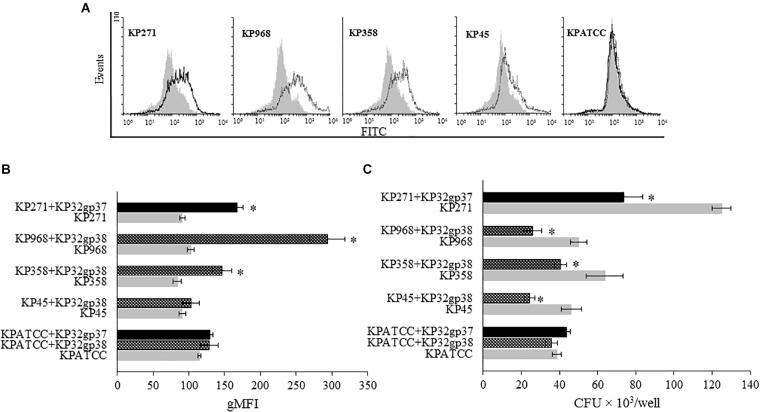
FIGURE 4.
Depolymerase-mediated phagocytosis of K. pneumoniae strains by the human monocyte cell line THP1 determined by flow cytometry (A,B) and plate counting (C). Representative flow cytometric plots: (A) histograms depict increased uptake of depolymerase-treated bacteria vs. untreated bacteria. UV-killed FITC-labeled K. pneumoniae (KP) strains 271, 358, 968, 45 and ATCC (non-K3/K21 serotype used as a control), preincubated or not with corresponding depolymerase, were mixed with monocytes at 100:1 ratio. Black peaks show the log of fluorescence intensity of monocytes exposed to depolymerase-treated K. pneumoniae strains; gray peaks depict log fluorescence intensity of monocytes exposed to untreated bacterial cells. (B) Quantification of ingested depolymerase-treated or untreated bacteria labeled with FITC by monocytes as measured by flow cytometry and analyzed using Flowing Software. Data are expressed as the geometric mean fluorescence intensity (gMFI) from the gated sample with phagocytozing cells ± SEM. Results are representative of three independent experiments. (C) Quantification of intracellular bacteria in THP1-differentiation macrophages infected with Klebsiella cells in the present or without corresponding depolymerase. The number of surviving bacteria was determined by macrophage lysis and colony count. Data represent the mean ± SEM of CFU × 103/well from three independent experiments performed in duplicate (n = 6). Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (∗P < 0.05) when compared to corresponding controls (no depolymerase, gray bars).