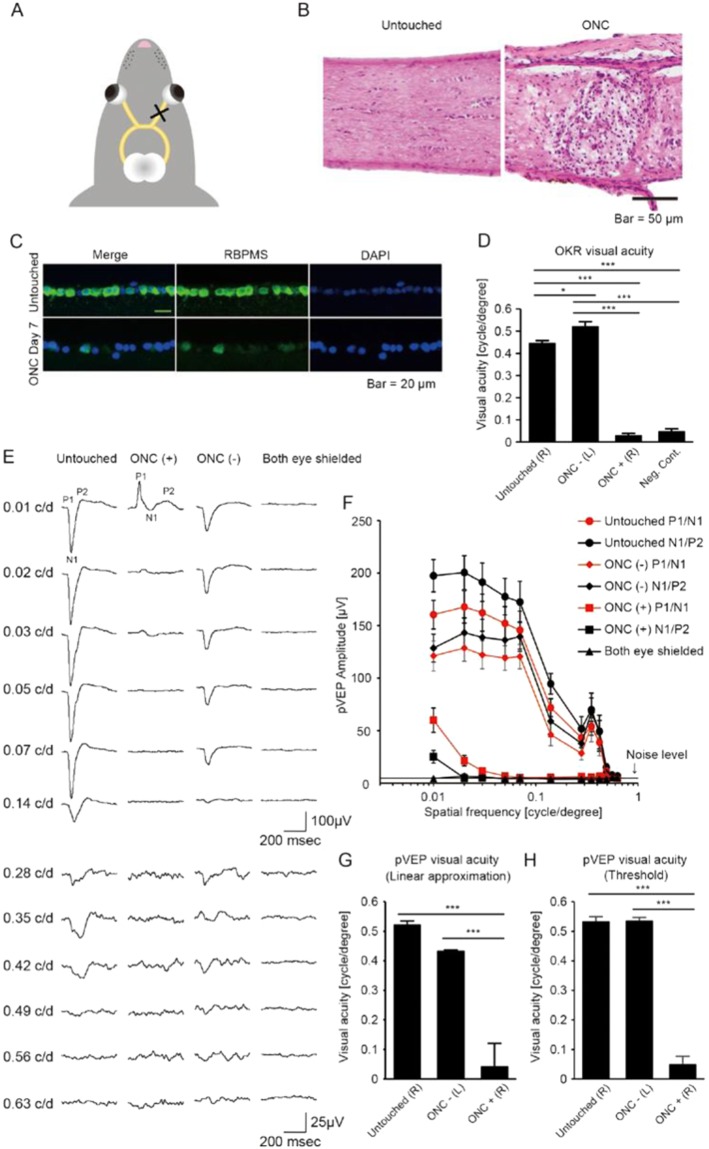
Figure 4.
Reliable detection of residual visual acuity in mice with severe optic nerve damage. (A) Schematic illustration of optic nerve crush (ONC). The right optic nerve was pinched with tweezers behind the globe. (B) Histological sections with Hematoxylin-Eosin staining of the optic nerve, untouched and after ONC (right and left, respectively). Note that ONC destroyed the tissue and led to the infiltration of inflammatory cells. Scale bar: 50 μm. (C) Histological sections of the retinal ganglion cell (RGC) layer in an ONC eye. Rbpms-positive RGCs (green) were fewer 7 days after ONC. Scale bar: 20 μm. (D) OKR-measured visual acuity in the ONC model. Optomotry could not detect residual visual acuity after ONC (ONC + (R)). Note that measured visual acuity after ONC is comparable to the background noise level of the system (Neg. Cont.; P = 0.883. N = 10 for untouched mice (untouched (R)), N = 10 for ONC mice (ONC – (L) and ONC + (R)), and N = 5 for Neg. Cont. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. (E) Representative pVEP traces recorded from the hemisphere contralateral to the ONC eye. pVEP from an untouched mouse and a blinded control (both eyes were shielded) are also shown. Note that the pVEP waveforms in the ONC mouse were very different from the untouched mouse. (F) Summary of pVEP amplitudes measured in ONC mice, shown as a function of the spatial frequency of the pattern stimulus. N = 9 for ONC mice, N = 7 for untouched mice, and N = 4 for mice with both eyes shielded. Noise level = 4.67 μV (N = 4). (G) Comparison of visual acuity in ONC and untouched eyes, as evaluated with linear regression of pVEP amplitudes. Note that visual acuity in the ONC eyes is lower than the untouched eyes. ***P < 0.01., N = 9 for ONC mice, N = 7 for untouched mice. Data represent mean ± standard error of the mean. Neg. Cont.: negative control. (H) Comparison of visual acuity in ONC and untouched eyes, as evaluated with threshold determination of pVEP responses. ***P < 0.001. ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer’s multiple comparison tests was applied for comparisons. Data represent mean ± standard error of the mean.